* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introdcution to ethics - MDC Faculty Home Pages
Paleoconservatism wikipedia , lookup
Neohumanism wikipedia , lookup
Internalism and externalism wikipedia , lookup
J. Baird Callicott wikipedia , lookup
Divine command theory wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg wikipedia , lookup
Value (ethics) wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Cultural relativism wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Ethics in religion wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Groundwork of the Metaphysic of Morals wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Kantian ethics wikipedia , lookup
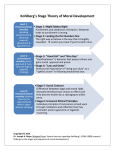
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
Utilitarianism wikipedia , lookup
School of Salamanca wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Morality throughout the Life Span wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to Ethics Moral Absolutism “I do, what I do, because, it’s the right thing to do.” ~ Jimmy Carter Sentimentalism “What is moral is what you feel good after, and what is immoral is what you feel bad after.” ~ Ernest Hemmingway Pragmatism “Truth is defined as whatever it is useful to believe.” ~ William James Faith “ For me, as for others, faith provided the meaning of life and the possibility of living”. ~ Leo Tolstoy Ethics • Ethics is the branch of philosophy that studies questions about right and good. • Moral theories provide a frame work for answering such questions and for evaluating human action. Are There Ethical Facts • It is a fact that the Rocky Mountains are located in North America. • Are there similar sorts of facts in ethics? • If so, why do so many people disagree about what is right and wrong. Ethical Skepticism • This view claims that moral knowledge is not possible. • This view claims that we cannot, as rational human beings, determine what is objectively right or wrong. Relativism • • • • • Species Relativism Descriptive Relativism Cultural Relativism Religious Relativism Individual Relativism Species Relativism • This view claims that ethics is relative to our species, or relative to humanity as a whole. Descriptive Relativism • Descriptive Relativism says that as a matter of empirical fact, different cultures have different beliefs about what is morally right and what is morally wrong. • This seems to be true. Cultural Relativism • This view claims that ethics is determined by each culture. What is right and wrong ought to be determined by culture. Religious Relativism • Morality is determined by God or religion. • This view is what many people subscribe to, however with more than 10,000 different religions which one is the right one? Individual Relativism (Subjectivism) • This view claims that each person ought to determine what is ethical for themselves. • As long as you do what you think is right, then you have acted correctly. Law vs. Morality Law Morality Immoral Laws? • Not all laws are moral. Morality may different across the world, but not all morals are equal! Value • What has value? Job Name What it Pays Minimum Training Needed New Jobs by 2014 1. Retail Salesperson $22,880 Short-term on-the-job training 736,000 2. Registered Nurse $55,680 Associate degree 703,000 3. Postsecondary Teacher $62,032 Doctoral degree 524,000 4. Customer Service Rep $29,350 Moderate-term on-thejob training 471,000 5. Janitor/Cleaner (NOT maids/housekeeping) $20,800 Short-term on-the-job training 440,000 6. Waiter/Waitress $15,980 Short-term on-the-job training 376,000 7. Combination Food Preparation & Serving Worker $17,850 Short-term on-the-job training 367,000 8. Home Health Aide $19,200 Short-term on-the-job training 350,000 9. Nursing Aid, Orderly, Attendant $21,890 Postsecondary vocational award 325,000 10. General & Operations Manager $93,580 Bachelor's degree plus work 308,000 Job Name What it Pays Minimum Training Needed New Jobs by 2014 1. Retail Salesperson $22,880 Short-term on-the-job training 736,000 2. Registered Nurse $55,680 Associate degree 703,000 3. Postsecondary Teacher $62,032 Doctoral degree 524,000 4. Customer Service Rep $29,350 Moderate-term on-the-job training 471,000 5. Janitor/Cleaner (NOT maids/housekeeping) $20,800 Short-term on-the-job training 440,000 6. Waiter/Waitress $15,980 Short-term on-the-job training 376,000 7. Combination Food Preparation & Serving Worker $17,850 Short-term on-the-job training 367,000 8. Home Health Aide $19,200 Short-term on-the-job training 350,000 9. Nursing Aid, Orderly, Attendant $21,890 Postsecondary vocational award 325,000 10. General & Operations Manager $93,580 Bachelor's degree plus work 308,000 11. Personal and Home Care Aide $17,560 Short-term on-the-job training 287,000 12. Elementary School Teacher $46,350 Bachelor's degree 265,000 13. Accountant and Auditor $57,160 Bachelor's degree 264,000 14. Office Clerk $24,440 Short-term on-the-job training 263,000 15. Hand laborer & freight, stock & material mover $22,190 Short-term on-the-job training 248,000 16. Receptionist and Information Clerk $22,900 Short-term on-the-job training 246,000 17. Landscaping and Groundskeeping Worker $22,260 Short-term on-the-job training 230,000 18. Truck Driver, Heavy and Tractor Trailer $34,920 Moderate-term on-the-job training 223,000 19. Computer Applications Software Engineer $78,570 Bachelor's degree 222,000 20. Maintenance and Repair Worker $32,290 Moderate-term on-the-job training 202,000 21. Medical Assistant $25,860 Moderate-term on-the-job training 202,000 22. Executive Secretary and Administrative Assistant $37,350 Moderate-term on-the-job training 192,000 23. Sales Representative, Wholesale & Manufacturing $54,500 Moderate-term on-the-job training 187,000 Value Concepts • Intrinsic Value • Extrinsic Value Intrinsic Value • Intrinsic value is value that a thing has in and of its self. • Often valuable as an ends. • Examples: • Happiness, Love, Honor, Family, Health, and Freedom Extrinsic or Instrumental Value • Something has extrinsic if it is valuable as a means to acquiring or attaining something we value in virtue of itself. • For example money has little or no intrinsic value, it’s just bits of paper or metal, but it has great extrinsic value in that it can used to acquire other items which we do value. Moral and Non Moral value • Moral evaluation is restricted to moral agents. • One must be a rational agent in order for one to evaluate the morality of your actions • These beings may still have moral worth. Non Moral Value • Objects, experiences, and states of affairs can all have value. They may have intrinsic or extrinsic value, but it is not moral value. • Some ethical theories evaluate actions in terms of how well they promote non moral value. Goals of a Moral Theory Theoretical Goals – Explains why something is moral. Practical Goals – Procedures for evaluating morality of action. Relation of Moral principles to Theory • Moral principles often encompass an expression of both theoretical and practical goals. • Example: “Act only on that maxim whereby you can at the same time will that it should become a universal law.” - Immanuel Kant Structure of Moral Theory • Theory of Right – Theories which focus upon right and wrong action. • Theory of Value – Moral Value – Non Moral Value Basic Moral Concepts • Deontological concepts • The prefix “deon” comes from the Greek and means duty. • Normative in nature- what we ought to do. • Obligatory Actions • Prohibited Actions • Optional Actions Obligatory Actions • • • • • Actions that one ought to do. Actions we have a duty to perform. They are required of us. They are the “right” thing to do. Failure to perform them means we have acted incorrectly, wrongly or immorally. Prohibited Actions • Actions that one ought not do. • Actions we have a duty not to perform. • It is required of us to refrain from performing them. • They are the “wrong” thing to do. • To perform them means we have acted incorrectly, wrongly or immorally. Optional Actions • Actions that are neither obligatory nor wrong. • We are not required to perform them • We are not required to refrain from performing them • Such actions are neutral Main Ethical Frameworks • Deontological Theories – Divine Command Theory – Kantian Ethics • Teleological Theories – Utilitarianism – Egoism – Hedonism – Virtue Ethics • Relativism Deontological Theories • Determine right or wrong on the basis of action • Divine Command Theory Teleological Theories • Also know as Consequentialist • Determine right or wrong on the basis of Consequences. • Utilitarianism • Egoism • Hedonism • Example: Robin Hood Deontological Theories • Kantian Constructivism Immanuel Kant Kantian Moral Theory • According to Kant our moral duty is knowable by means of our rationality. Our rationality allows human beings to be conscious of rules of behavior, which he considers to be both Universal and Necessary. Categorical Imperative • Categorical Imperative- It commands certain conduct immediately. • Categorical- it applies instantly to all rational beings • Imperative- a principle on which we ought to act • "Act only on that maxim whereby thou canst at the same time will that it should become a universal law". A Rule of Logic • Lying, Cheating, Stealing and Killing are all wrong for Kant. • However they are wrong, not based upon the consequences, but because according to Kant, they violate a rule of logic. • For Example, if we all lied, all the time, then there would be no truth in the world. As such, truth would be meaningless- Logically, it would not exist- as a consequence… hard to avoid speaking in Terms of consequences. • Kant thinks that certain moral rules apply to everyone all the time. A rule such as lying is wrong, applies to everyone, and therefore morality commands that we never lie no matter what situation we find ourselves in. The beneficial consequences of our action do not justify any action that violates the categorical imperative. Plato 428-384 B.C. • Plato, the student of Socrates, founded the first University in the year 387called the Academy. • Science and knowledge were the chief goals of study. • The mind was trained to cut thru rhetoric. Division of the Soul • According to Plato the soul is divided into three parts. • Tripartite conception of the soul. • Reason • Spirit • Appetite Reason • Reason guides us rationally towards reasonable goals Spirit • Spirit gives us the ability to comply with reason, to be brave and follow thru with our goals Appetite • The appetitive side of our soul drives our impulses and desires. • Reason, according to Plato, must keep the desires in check. • Allowing our passions to make decision will lead to chaos and ruin. Plato and ignorance • Ignorance leads to evil. • Plato claims that no one knowingly does wrong. • Akrasia- or weakness of the will, does not exist. • People simply do not understand the harm they are doing by performing certain actions. Teleological Theories • Focus on the consequences of actions. • Right actions are equated with those that produce things of value. Utilitarianism • Utilitarianism- an act is good if it maximizes the greatest amount of good. Jeremy Bentham Quantitative Utilitarian Bentham claims that: • "Nature has placed mankind under to sovereign masters, pain and pleasure. It is for them alone to point out what we ought to do, as well as determine what we shall do" Principle of Utility • By the principle of utility he means, "that principle which approves and disapproves of every action whatsoever, according to the tendency which it appears to have to augment or diminish happiness". Hedonic Calculus • • • • • • • Acts of pleasure- consider Intensity Duration Certainty Propinquity- nearness ConsequencesFecundity- the chances that it will be followed by more of the same, purity- the chances that the pleasure will not be followed by pain • Extent- the number of people it affects John Stuart Mill Qualitative Utilitarian Quality over Quantity • "It is better to be Socrates dissatisfied than a fool satisfied...It is better to be a human being dissatisfied than a pig satisfied." Mill Claims: • Mill claims that the Hedonic calculus is impossible because the nature of pain and pleasure are such that no meaningful standard can be established to weigh one pleasure against one pain. • He thinks that QUALITY pleasures will lead to a greater quantity of pleasure. Act utilitarianism • Same as “utilitarianism” • An act is right if and only if no other act available to the moral agent maximizes utility more than the act decided upon. Rule utilitarianism• An act is right if and only if it falls under a correct moral rule. • So not only must the act have good consequences it must not violate any moral rules. • Rules are justified in terms of the social utility that results in the long term by obeying them. Not Egoism • "The happiness which forms the utilitarian standard of what is right conduct, is not the agents own happiness, but that of all concerned..." In this way, the rightness or wrongness of an act is not based upon the consequences of pain and pleasure for yourself, but also those consequences for others. Ethical Egoism • Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679) • Ethical Egoism- each person ought to pursue his self interest exclusively • Psychological Egoism- each person does pursue his own self-interest exclusively Ethical Hedonism • Epicures (341- 270 BC) claimed that the right action is the one that leads to the most pleasure for the individual. Yet instead of seeking out pleasure, Epicures says that we should try to avoid pleasure that way we will not feel too bad when we are without them. He proposes a minimalist philosophy where we seek only that which we need to survive. J.J.C. Smart • Is a modern day hedonist. • He proposes and interesting example. Imagine that we could all be plugged into a machine that can stimulate the pleasure centers in our mind. All we have to do is push a button and we will experience tremendous pleasure. Life of a button pusher. • If pleasure is the chief goal of life, then what do we say about the life of a button pusher- one that sits back in his easy chair and pushes a button all day long. Further imagine that our society has progressed to a point technologically where we don't have to work, so all of the button pusher are not going to starve to death and our civilization is not going to be destroyed. Would such a way of life be laudable? Would it be worthy of pursuit? Stoicism • Stoics would seek hardship so that they could train themselves to remain untroubled by pain and hardship. • They claimed that the universe was governed by natural law, that there was a purpose and reason for all things. Stoicism continued Whatever happens is the inevitable outcome of the logic of the universe. Whatever happens, happens with a reason and is therefore for the best. Given that you cannot control your fate, but you can control your attitude, remain emotionally uninvolved in your fate, and your life will be untroubled. Arthur Schopenhauer • Held that the world is structured according to will, that nothing can bring meaning to our existence. Life is negative • Schopenhauer argues that the nature of human existence is such that it is impossible to experience to have positive experience. • He claims that life is pointless because our choices of ends or goals are entirely arbitrary. Can’t fulfill our desires • He claims that what we consider good is simply things that are those things that aid in the satisfaction of our will and those things that are bad are those which get in the way of our satisfaction of our will. • He says that it is impossible for our desires to be fulfilled because the fulfillment is transitory- the moment our appetite is sated another desire appears and we are left with nothing. Desire is Negative • That is why he claims that desire is something negative. • Schopenhauer’s main point is that nothing can really ease our suffering in this existence except death. Leo Tolstoy "Confessions" • Faith vs.. Reason • The notion that faith is irrational has long been pervasive in philosophy. The dichotomy between faith and reason dates back to antiquity and was taken for granted by medieval thinkers such as St. Augustine and St. Thomas Aquinas. Rationality leads to nothing • He says, "philosophical knowledge denies nothing but simply replies that is cannot solve the question, and that as far as it is concerned any resolution remains infinite. Having understood this, I realized that it was impossible to search for an answer to my questions in rational knowledge; … rational knowledge had led me to recognize that life is meaningless. My life came to a halt and I wanted to kill myself. Faith Gives Purpose • As I looked around at people, at humanity as a whole, I saw that they lived and affirmed that they knew the meaning of life. I looked at myself, I had lived as long as I knew the meaning of life. For me, as for others, faith provided the meaning of life and the possibility of living." Friedrich Nietzsche "What is Noble" • Slave morality vs. Master morality • The weak hold the Slave Morality – Claims all are equal, all deserve fairness. • The powerful hold the master morality. – A Morality of nobility where cunning and pride are held in highest regard. Denies equality. Nietzsche claims that the wool has been pulled over our eyes, equality and fairness are a joke Jean-Paul Sartre • "Existentialism and Humanism" • 1) existence comes before essence. • 2) Man is free- that is he posses free will and as such is necessarily free • 3) Each man determines his own morality. Intuitionist • W.D. Ross Prima Facie Duty • Prima Facie duty vs. absolute duty • A prima facie duty is a conditional duty. It may be overridden by a duty of greater importance. Prima Facie duties are not static. This means that one may out weight another in one situation and the same two duties might switch positions given other circumstances. We know which one takes precedent by intuition- we just know. Not Quite Utilitarianism • Example: • Keeping a promise – Utilitarian, act utilitarian, keep the promise if it produces beneficial consequences – Keep the promise, because you have a moral duty to keep them promise, unless a greater duty comes into conflict with keeping your promise. Sentimentalism • The Notion that our sentiments or feels can be used to determine morality. • Very similar to intuitionism. • David Hume is often viewed as an ethical sentimentalist this is very similar to W.D. Ross. Aristotle’s Virtue Ethics Eudaimonia • Aristotle argues that happiness is the goal of life. Happiness, Greek: eudaimonia, means human flourishing, or living well or doing well. Happiness and Function • Human happiness if tied to human function. Aristotle feels that we will be happy if we are all fulfilling our function. Further he thinks that everything has a function. The function of something is whatever makes that thing good. Something is good according to Aristotle if it fulfills its function. A good knife is one that cuts well. Function of a person • What is a good person? Aristotle says that the function of man is rationality . Therefore a good man is one that is rational. A rational man is controlled by reason in all things. Reason as our guide • To be happy we must be “acting in accordance with right reason.” The rational part of the soul must be in control of our appetites. Golden Mean • .It is for this reason that Aristotle discusses the golden mean. The golden mean is the balance between excess and deficiency. • Foolhardy Courage Cowardice • Gluttony Temperance Starvation • Greed Ambition Sloth • Indulgence Temperance Insensibility Natural Rights Theorist • Thomas Hobbes • John Locke • Jean Jacques Rousseau Thomas Hobbes State of Nature • Mankind was born into the state of nature. Life in the state of nature is "short nasty and brutish". State of Nature Continued • There are no arts or letters only a war of all against all. In this state men all have an equal right to everything. Right is equal to freedom, the freedom, to do what he would, and against whom he thought fit, and to possess, use and enjoy all that he would or could get. 1 Natural Right • Thomas Hobbes • 1 Natural Right- LIFE! Two Laws of Nature • Hobbes says that in the State of Nature mankind knows by reason two laws of nature, they are 1)"seek peace and follow it" and 2), "be willing to lay down his right to all things; and be contented with so much liberty against other men, as he would allow against himself." • “Golden Rule” Form a Government • The best way to protect your RIGHT to life. • All people give up our rights, to the king. • King determines morality. • NO IMMORAL LAWS! John Locke Kinder, Gentler state of Nature • Locke’s conception of the state of nature differs from Hobbes. He says that it is , "Men living together according to reason, without a common superior on Earth with authority to judge between them is properly the state of nature". John Locke: 3 Natural Rights • Natural rights are akin to human rights. • LIFE • LIBERTY • PROPERTY Jean Jacques Rousseau True State of Nature • Rousseau claims that both Hobbes and Locke mischaracterize the state of nature. • Natural Man • Civil Man Natural Man • Natural man is motivated by love of self, only cares about self preservation. Natural man is not motivated by greed or love of material goods. Civil Man • Mankind moves from the state of nature to civilization once we move from self preservation towards the goal of acquiring property and wealth. At this point mankind becomes motivated by greed and corrupted by envy. Mill’s Harm Principle • The Harm Principle : ...the sole end for which mankind are warranted, individually or collectively, in interfering with the liberty of action of any of their number, is selfprotection. That the only purpose for which power can be rightfully exercised over any member of a civilized community, against his will, is to prevent harm to others.