* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lect 2 Evolution
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
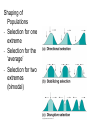
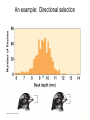
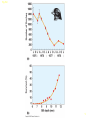
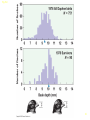
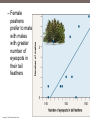
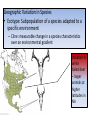
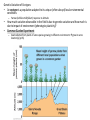
Lecture 2 Evolution and Ecology ‘Nothing in biology makes sense, except in the light of evolution.’ Dobzhansky 1 Ecosystem Structure and Evolution • Niche: functional role an organism plays in an ecosystem…. • • ‘the sum total of all activities and relationships in which individuals of a species engage as they secure resources necessary to survive and reproduce’… job or role in an ecosystem Adaptation: ‘a genetically determined characteristic that … improves fitness Fitness: the ability to leave reproductively viable offspring 2 • What is evolution? • Why is it important for species to evolve? • ‘Evolution is a population thing’: Individuals do not evolve occurs over generations in populations. ‘descent with modification’ (see page 645) 3 Evolutionary thought: Charles Darwin/Alfred Russell Wallace Thomas Malthus: social philosopher Charles Lyell: geologist/natural philosopher 4 Natural selection: Selection in a genetically variable population for those with traits which favor survival and reproduction: 1. Over reproduction 2. Struggle for existence – competition for resources 3. Differential survival and reproduction Fitness: ‘the ability to survive and leave reproductively viable offspring 4. Genetic variation Adaptation: a trait that is possessed by an individual enables an enhanced ability to survive and reproduce 5 Evolution has a genetic basis: Genes are heritable units that determine traits Variation in genes occurs naturally: due to mutation Alleles Gene Pool: the total collection of gene/alleles within a population Changes in the gene pool changes in a population 6 Shaping of Populations • Selection for one extreme • Selection for the ‘average’ • Selection for two extremes (bimodal) 7 An example: Directional selection 8 Fig. 5-8 9 Fig. 5-9 10 Stabilizing Selection: average is favored Goldenrod gall size – formed by fly Small: attacked by wasp Large: attacked by birds Species have become specialists feeding on seed providing optimal energy efficiency Disruptive Selection: Specialist forms develop Adaptive Radiation: Single ancestral from give rise to multiple ‘specialist’ forms Sexual selection: an aspect of natural selection • A process in which (usually) females select amongst potential mates • Example - Peacocks: female selects males with large, bright, colorful tails- why? Handicap hypothesis • Operates in plants too – competition for pollinators various mechanisms to lure pollen transferring animals 14 Sexual selection – an aspect of natural selection: includes two aspects Intrasexual: males compete - selection leads to evolution of structures used in combat with other males – Deer’s antlers or ram’s horns, bright colors, etc. – selective pressure is for ability to compete successfully with members of same sex Intersexual selection- Females select amongst winners – agents of selection – Selection based on various cues – appearance and behavior – goal (evolutionary sense) select mate with best fitness Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. – Female peahens prefer to mate with males with greater number of eyespots in their tail feathers Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Evolution without natural selection - Genetic drift: • Genetic drift refers to fluctuations in allele frequencies in a population arising from chance events. • Most pronounced in small populations resulting from Founding events Natural disasters High levels of predation - bottlenecks • Random: population not selected based on adaptations 17 Other processes leading to evolution: Genetic drift: Changes in allele frequencies across generations due to chance events: • Random disturbances • Small populations • Founder effects 18 Natural Selection Can Result in Genetic Differentiation • The geographic range of a species can result in phenotypic variation of neighboring populations • A wider geographic range includes a broader range of environmental conditions • In general, the greater the distance between populations, the more pronounced the phenotypic differences Geographic Variation in Species • Ecotype: Subpopulation of a species adapted to a specific environment – Cline: measurable change in a species characteristics over an environmental gradient Variation in white tailed deer – larger animals at higher latitudes in NA Genetic Variation of Ecotypes • An ecotype is a population adapted to its unique (often abrupt) local environmental conditions – Yarrow (Achillea millefolium) response to altitude • • How much variation observable in the field is due to genetic variation and how much is due to impact of environment (phenotypic plasticity)? Common Garden Experiment – Seed collected from plants of same species growing in different environments grow in same location(s) (p 85) • Geographic isolates result when gene flow among subpopulations is prevented • The isolation is rarely complete, and so these isolated subpopulations are often classified as subspecies because of a set of unique characteristics • Example: Ensatina spp. of California – a ‘ring species‘ http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/0_0_0/devitt_02 Summary: • Evolution involves heritable differences amongst individuals in a population which ultimately impact fitness • Organisms become ‘tailor made’ for their niche within an environment by processes of evolution • Characteristics of individuals making up current populations are a product of natural selection in ancestral populations 23