* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 23 Notes
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
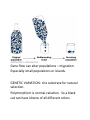
Ch 23 – Notes Evolution in Populations Smallest Unit that can evolve is a population. Definitions: Populations: a localized group of individuals belonging to the same species. Gene Pool: All genes in a population. Species: A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Hardy-Weinberg studied evolution in populations. Hardy-Weinberg theorem: The frequencies of alleles and genotypes in populations remain constant in generations – UNLESS acted upon by agents* other than Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles. What *agents can cause the gene pool to change? Mutations Natural Selection Migration Non-Random Mating Genetic Drift (chance events that can change a population) Populations must be big Microevolution: Changes in the gene pool on the smallest scale. Genetic Drift can lead to microevolution. Examples: Accidents, part of the population getting separated (founder effect), chance events… Gene flow can alter populations – migration. Especially small populations or islands. GENETIC VARIATION: the substrate for natural selection. Polymorphism is normal variation. So a black cat can have kittens of all different colors. Geographic Variation: Organisms can vary depending on where they live. Sexual Dimorphism: Males and females look different. Some animals have a huge dimorphism (peacocks and peahens, sealions, praying mantis). Intrasexual selection: males compete for the females. The Perfect Animal? No… 1) Evolution is limited to history… you have to have the genes to begin with. Evolution can only “edit” existing variations. 2) Adaptations are often compromises… 3) Not all evolution is adaptive… sometimes the adaptations are good… sometimes not… sometimes the survival of the lucky…