* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory and Viruses - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
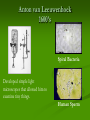
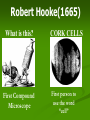
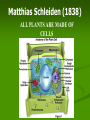
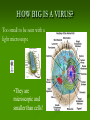
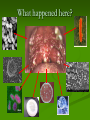
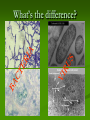
Aim: How was the cell theory developed? CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Cells: Metabolism: Homeostasis: Reproduction: What instrument was vital for scientists to discover and learn about cells? Light Microscope A light microscope can magnify objects up to 1000 times. This instrument allows scientists to see larger parts of a cell (cell membrane, nucleus, chromosomes, etc…) Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1600’s Spiral Bacteria Developed simple light microscopes that allowed him to examine tiny things. Human Sperm Robert Hooke(1665) What is this? First Compound Microscope CORK CELLS First person to use the word “cell” Matthias Schleiden (1838) ALL PLANTS ARE MADE OF CELLS Theodor Schwann (1838) ALL ANIMALS ARE MADE UP OF CELLS Rudolf Virchow (1858) CELLS COME FROM PRE-EXISTING CELLS Cell theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function (metabolism) New cells come from preexisting cells What are some problems with the Cell Theory? Are viruses living? Where did the first cell come from? Mitochondria and Chloroplast can reproduce on their own. Viruses They are not made up of cells, but are they living? What do you know about viruses? They can make you very sick They can be transmitted from person to person There are different types of viruses HOW BIG IS A VIRUS? Too small to be seen with a light microscope •They are microscopic and smaller than cells! Electron Microscope Used to view extremely small structures inside cells & viruses Utilizes an electron beam instead of a light beam Can magnify up to a million times Subject must be dead and dry How can we determine if a virus is living or non-living? Is it made of cells? Does it maintain homeostasis? Does it carry out metabolism? Does it reproduce? Is a virus living or non living? Introduction to Viruses Video What do all cells have in common? Cell membrane – gives shape to the cells and allows things in and out. The cytoplasm – the jelly like material where all cell parts are found Light Microscope Our microscope has a maximum magnification of 400x. Useful for viewing larger organisms like bacteria and paramecium. What happened here? Why does a doctor stick a swab inside your mouth? Cultures are used to grow bacteria. The jelly at the bottom is called agar. Why do we need agar to grow bacteria? What’s the difference? What if you want to separate a mixture? Use A Centrifuge Janet Plowe Cell Membrane Gives shape and controls what comes in and out