* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory, Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
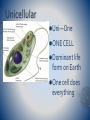
Warm-Up #2 10/8/12 1) What does the word cell mean? 2) What do cells make? 3) Is this alive? Why/Why not? 4) Is this alive? Why/why not? Unit 2 Tests & Unit 3 Vocab Label your grade sheet to reflect the unit 2 test and your current grade in class. Once you get your test back, you will make corrections to get back 1 point for each missed You must write out the entire question and answer to get credit. Do this on your own paper!! Complete your vocab list when finished with the test Cell Theory, Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, Multicellular, Unicellular What We’re Going To Learn… Essential Question : Does the basic understanding of a cell give an understanding of life? I Can: Differentiate between : prokaryotes and eukaryotes Cell Theory and Contributors Multicellular and unicellular Cells and Scientists Cells are the basic units of life. Mathias Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells. Theodor Schwann concluded that all animals were made of cells. Rudolph Virchow proposed that all cells come from existing cells. Together these discoveries make up the cell theory. Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. Multicellular Multi--Many More than one cell Cells must work together Cells specialize – do special jobs Unicellular Uni—One ONE CELL Dominant life form on Earth One cell does everything Cells Cells fall into two categories Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Prokaryotes NO NUCLEUS The genetic material is a simple DNA chain in a circle NO Membrane-bound organelles Cells are small Cells are simple Unicellular Ex. Bacteria Eukaryotes NUCLEUS The genetic material is found inside the nucleus Membrane-Bound organelles Cells are larger Cells are more complex Can have 1 or more cells (multicellular) Examples: Plants, animals, protist and fungi Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes All cells have: Cell membrane DNA at some point in their lives Ribosomes Is It Alive? How do you know one is alive and the other isn’t. Make a list with your partner. Earthworm Gummy Worm Characteristics of Life To be living must…. 1. Made up of cells or cell parts 5.Maintain Homeostasis 2. Response to Stimulus in the environment 6.Ability to Reproduce 3. 4. Obtain and use energy (Autotrophs /Heterotrophs) Grow and Develop 7.Adapt over time 8.Universal Genetic Code or DNA