* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title goes in here
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
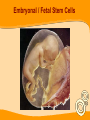
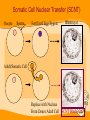
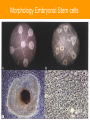
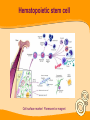
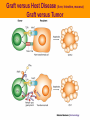
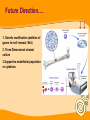
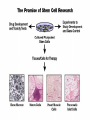
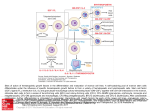
Stem Cells: Roadmap to the clinic Negar Azarpira, MD Associate professor of Pathology 14 April 2010 ■■■■ Why it is Important? ■■■■■■■■ Is It As A New Drug? Stem cell Definition • Unspecialized cells in human body that are capable of becoming specialized cells, with new specialized cell function. • Very broadly, they divided in two major groups: • Embryonal/Fetal SC • Adult SC • Best example: Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) Sources of Human Stem Cells Embryonal / Fetal Stem Cells Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC) Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) Oocyte Sperm Fertilized Egg/Zygote Blastocyst Adult/Somatic Cell Replace with Nucleus From Donor Adult Cell SCNT Blastocyst Morphology Embryonal Stem cells Advantages - Unlimited self renewal Commercially Cell lines Pleuripotent High Telomerase activity & Low chromosomal instability Clinical Application • Transplantation of differentiated cells • Pharmaceutical screening • Study oh development & congenital anomaly Adult Stem cell Hematopoietic stem cell Cell surface marker/ Florescent or magnet Hematopoietic stem cell • CD34+ : 0.5-5% of Bone marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation • Outologus or Allogenic • HLA matching■ • • • • Source of Hematopoietic cells: Bone marrow (GM-CSF,…) Mobilized peripheral blood Umbilical cord blood Graft versus Host Disease (liver, Intestine, mucosa) Graft versus Tumor Clinical Application • • • • Treatment of hematological malignancy Inherited disease (SCID), β Thalasemia Mediate tolerance for Solid organ allograft Vehicle for gene Transfer Future Direction…. ↓↓ 1. Genetic modification (addition of genes for self renewal, Wnt) 2. Three Dimensional stromal culture 3.Supportive endothelial population or cytokines Other interesting cells in bone marrow • CD133 + : Endothelial precuresure • Mesenchymal cell The most common phenotypical markers: CD90, CD73, and CD105 Mesenchymal stem cells - 0.01-0.001% of Bone marrow cells - Has Immunomodulaory properties -Animal study: Skin graft, BMT (GVHD↓) - Human study: Bone marrow graft Crohn’s disease Islet cell transplant First Stem Cell Drug Prochymal • Prochymal is a preparation of mesenchymal stem cells, obtained from the bone marrow of healthy young adults • The first SC product approved by the FDA as pharmaceutical product • The target disorders of this therapeutic are GVHD and Crohn’s disease • For the repair of heart tissue following a heart attack • For protection of pancreatic islet cells in patients with type I diabetes • For the treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) • Osiris Therapeutics, Inc Reprogramming induced pleuripotent stem cell (iPS) By ectopic expression of transcription factors by retroviral transduction can reprogram somatic nuclei to the pleuripotent state. In the future…. • With Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine: Can Help patients with Stroke, Myocardial infarction, Cord injury, Diabetes, Cirrhosis , Parkinson… Bioethics Reference Stem cell from bench to bedside Bongso A & Lee E.H 2005 Thank you for your attention Thank you for your attention..