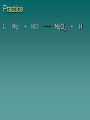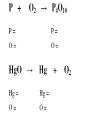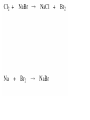* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
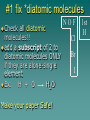
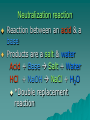
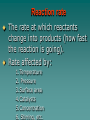
Chapter 7 Chemical Equations Chemical Reaction one or more substances are changed to new substances (a chemical change occurs) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) reactants products -substances -new substance about to react formed (l)=liquid, (g)=gas, (cr)=crystalline solid, (aq)=aqueous solution Law of Conservation of Mass The starting mass of reactants equals the final mass of the products “Mass is neither created nor destroyed” Chemical Equations Represents the substances involved in a chemical reaction 2H2 + O2 2H2O Chemical Equations 2H2 + O2 2H2O –coefficient- represents the relative amounts of substance taking part in a reaction –subscript- tells the # of atoms –Arrow () - “yields” or equals Balancing Equations The goal is to get the # of atoms of each element equal on both sides of the reaction! #1 fix *diatomic molecules Check all diatomic molecules!! add a subscript of 2 to diatomic molecules ONLY if they are alone-single element Ex: H + O H2O Make your paper Safe! NOF Cl Br I 1st H #2 Check for balancing Example: NaCl Na 1 Cl 1 Na + Na 1 Cl 2 Cl2 #3 Add coefficients where needed –Do not change subscripts … Ever, never ever –Coefficient is multiplied through the formula it is in front of –Use lowest possible coefficient Example: 2 NaCl Na Cl 12 12 2 Na Na Cl + 12 2 Cl2 Helpful Hints Treat polyatomic ions as a unit IF it appears on both sides. Leave elements like hydrogen, oxygen, etc. until last. If there is an even # on one side and an odd # on the other, look for the lowest common multiple. Practice 1. Mg + HCl MgCl2 + H 2. (NH4)2SO4 + Ba(NO3)2 BaSO4 + NH4NO3 3. H2O2 H2O + O2 4. AgNO3 + KCl AgCl + KNO3 You do the last two on your own! Star Questions When one or more substances are changed to new substances we call this a? Chemical reaction represents the relative amounts of substance taking part in a reaction Coefficients Examples are H2, N2, O2, F2 Diatomic molecules Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis –2 or more substances combine to form another substance (one product). Can be single elements or compounds! A + B AB + Cl NaCl Example: Na “boy dates girl = happy couple” In the cartoon, the skinny bird (reactant) and the worm (reactant) combine to make one product, a fat bird. Decomposition – one substance breaks down into 2 or more simpler substances AB A + B Na + Cl Example: NaCl “happy couple breaks up into just guy and girl again” In this cartoon the egg (the reactant), which contained the turtle at one time, now has opened and the turtle (product) and egg shell (product) are now two separate substances. Single replacement – one single element replaces another in a compound A + BC AC + B HCl ZnCl + H Example: Zn + “home wrecker” Notice, the guy in the orange shirt steals the date of the other guy. So, a part of one of the reactants trades places and is in a different place among the products. Double replacement –Two compounds exchange positive ions to form two new products AB + CD AD + CB Example: AgNO3+ NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 “JBHS Prom, change of hearts, swingers, dating Jerry Springer style” Star Questions In a synthesis reaction how many products are formed? 1 What type of reaction is it when one single element replaces another in a compound? Single replacement Neutralization reaction Reaction between an acid & a base Products are a salt & water Acid + Base Salt + Water HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O *Double replacement reaction Combustion Reaction A reaction in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, often produces heat & light *Products are always carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Energy & Reaction Rates Chemical reactions break chemical bonds in reactants & form new bonds in products. Chemical energy—energy stored in chemical bonds Breaking bonds absorbs energy Forming bonds releases energy Endothermic reactions More energy is needed to break chemical bonds, so it absorbs energy from its surroundings! It’s surroundings would feel cold, because heat (energy) is being taken from it. Example: Melting ice….. Energy is absorbed from the surroundings to melt the ice, which makes the air nearby feel cold. Exothermic reactions Forming chemical bonds releases energy into its surroundings The energy released by forming products is GREATER than the energy required to break the reactant’s bonds It’s surroundings would feel hot, because heat (energy) is being released. Conservation of energy the amount of total energy before & after the reaction is the same. Reaction rate The rate at which reactants change into products (how fast the reaction is going). Rate affected by: 1.Temperature 2. Pressure 3.Surface area 4.Catalysts 5.Concentration 6. Stirring, etc. Catalysts a substance that affects the reaction rate w/o being used up in the reaction. Star Questions Explain a neutralization reaction. Acid & base combine to form salt & water, double replacement reaction Explain a combustion reaction. A reaction in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, often produces heat & light, *Products are always carbon dioxide & water