* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genomics Core, Dr. Yuannan Xia
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
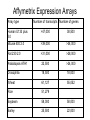
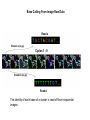
Affymetrix Microarray and Illumina/ Solexa NextGen Sequencing Yuannan Xia, Ph.D Genomics Core Research Facility 10.27.2009 Affymetrix GeneChip Microarray System 1. High density oligo array: a single array containing 1 – 6 million features generates 1 – 6 million probe hybridization data points for summaring to values of 20K – 50K genes. 2. Hybridization Oven 640: Hybridize samples to array 3. Fluidics Station 450 : washing and staining 4. Scanner 3000 7G: Confocal laser scanning; High pixel resolution at 0.5 micron level 5. Data generating and processing software: GCOS Software pipeline for data mining and annotation: Bioconductor Rosetta, AffyMiner, Ingenuity, Netaffix Affymetrix Expression Arrays Array type Number of transcripts Number of genes Human U133 plus 2.0 >47,000 38,500 Mouse 430 2.0 >39,000 >34,000 Rat 230 2.0 >31,000 >28,000 Arabidopsis ATH1 22,500 >24,000 Drosophila 18,500 18,000 Wheat 61,127 55,052 Rice 51,279 Soybean 58,000 58,000 Barley 25,500 22,000 Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer II System Flow cell – A glass slide with 8 channels (lanes) and 16 manifold ports for performing all PCR and sequencing reactions inside each channel. Cluster generation station – Perform PCR bridge amplification to generate clusters inside the channels of flow cell and prepare flow cell ready for sequencing GAII and Paired End Module – Perform sequencing, imaging, cluster modification for paired end read 2 sequencing Two Key Chemistries used in Solexa Sequencing Technology 1. PCR bridge amplification of individual templates in a shotgun library to generate clusters (DNA polymerase colony) High cluster density: 10 – 20 million/Lane 80 – 150 million/Run 2. Reversible Terminator Sequencing Chemistry Allow to incorporate only ONE nucleotide at each cycle Generate accurate (>99.5%) sequences: 300 – 800 Megabases/lane 3 – 6 Gigabases/Run Bridge Amplification of Individual Templates by PCR Cluster Generation Sequencing by Synthesis Using Reversible Terminators >All 4 bases with Reversible Terminators >4 labeling colors >Terminators can be removed >Add all 4 nucleotides in one reaction >No problem with homopolymer repeats >Higher accuracy Steps of Sequencing by Synthesis A B C D A. Extend first base T, read, and deblock. B & C, Repeat step A to extend strand. D. Generate base calling. Base Calling From Image Raw Data Read a Cluster-a (xa,ya) Cycles 1 - 9 Cluster-b (xb,yb) Read b The identity of each base of a cluster is read off from sequential images Solexa Sequencing Applications at UNL Genomic Resequencing Yeast genome (V. Gladyshev; AGP Corn Processing) Fugus genome Aspergillus (S. Harris) ChIP Sequencing Arabidopsis CHlP DNA (Fromm; Cerutti) mRNA Sequencing - Transcritome Arabidopsis transcriptom (H. Cerutti) Human KSHV cell transcrptome (C. Wood) Chlorella/Virus transcriptome (J. Van Etten) Mole rat transcriptome (V. Gladyshev and D.Fomenko) Fugus Aspergillus transcriptome (S. Harris) Paired End Sequencing Arabidopsis mitochondrial genome (S. Mackenzie) Small RNA sequencing Several UNL faculty have expressed strong interest. (Y.Bin, H. Cerutti, J. Mower, J. Alfano) Genomic Resequencing Data of Resequencing of 19 yeast genomes Nucleus Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing Crosslink (ChIP-seq) IP Genome-wide analysis Sequencing Map binding sites • Gene Regulation and Control • Epigenetic modifications • DNA-protein interactions Transcriptome Analysis – mRNA-Seq •Relative expression of transcripts •Analysis of splice variants/coding SNPs •Analysis of non-coding RNAs •Transcript discovery Paired End and Mate Pair Sequencing Provides long range information – Repeat sequences – Characterize copy number variants & rearrangements – De novo assembly Increases output per flow cell Workflow of the service Genomic DNA, total RNA, CHlP DNA (exp design, QC) DNA shotgun library preparation (SR, PE, cDNA) Cluster generation (35 PCR amplification cycles) Sequencing of clusters on GAII (1 TB machine, sequencing, imaging, image processing, base calling) Data analysis on remote server at Bioinfornatics Core Facility (8 TB machine, base calling , read alignment using Illumina pipeline software) Cost of Gene Expression Profiling Microarray • $500 - $650/array/sample • $3000 - $4000 for 2 treatments-3replicats 6 samples experiment (6 arrays) Illumina • $1300/lane/sample (400Mb sequence), $2100/2 lanes/sample (800Mb) • $ 4200 for 2 treatment 2 samples 4 FC lanes experiment (without replicates) Challenges More than 40 billion nucleotide sequences have been generated, will be double soon. Need solutions to - Sample preparation (e.g small RNA libraries, CHlP pulldown) - Further extracting sequencing data - Biological annotations - Data storage and management - Drafting publications Budget: - Maintaining both Affymetrix System and Illumina Solexa System is expensive. - Cost for upgrading the system. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dr. Mike Fromm Drs. Jean-Jack Riethoven Ms. Mei Chen