* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
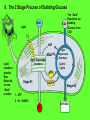
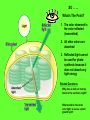
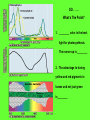
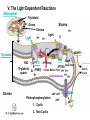
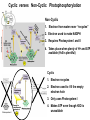
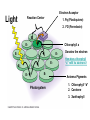
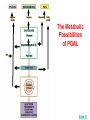
Photosynthesis: Nature’s Greatest Gift to Life I. A Historical Perspective: CO2 + H2O C6H12 O6 + O2 A. Old View: CO2 is Split, H2O stays intact Why this Explanation Made Sense CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + 1. Oxygen stays as a gas in the same ratio 2. Water has a 2:1 ratio as the carbohydrate O2 B. New View: Water is Split, CO2 stays intact CO2 + H2 O C6H12O6 + O2 Why the change in views? 1. When water was tagged with an O2 isotope , the tag was on the released O2, not the glucose CO2 + H2O 2. C6H12O6 + O2 When CO2 was tagged with the O2 isotope, the tag was found in the glucose, not the released O2 CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 The Structure Leaf and Photosynthesis SO . . … Tissue What’s The Point? light chlorophyll enzymes Organ Cell Organelle 1. The structures of a leaf must provide for the function of photosynthesis 2. The chloroplast is the functional unit of photosynthesis II. The 2 Stage Process of Building Glucose The “Dark” Reactions are CO2 building Glucose from CO2 H2O Light ADP NADP Light reactions provide Raw Materials for the “Dark” reaction Light Dependent reactions Light Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP Stage #1 NADPH Stage #2 1. ATP 2. H+ (NADP) O2 C6H12O6 III. Energy from Light (I hope you remember your physics) SO . . … What’s The Point? 1. Visible light comes in different wave lengths and energy levels 2. The pigments seen are due to different wavelengths and energy levels “Not all wavelengths are created equal” SO . . … What’s The Point? 1. The color observed is the color reflected (transmitted) 2. All other colors are absorbed 3. Reflected light cannot be used for photosynthesis because it does not absorb any light energy Related Questions Why does a dark car heat up faster in the sun than a light? What would be the worst color light to use as a plant growth light? SO . . … What’s The Point? 1. ________ color is the best light for photosynthesis. The runner-up is ________ 2. The advantage to having yellow and red pigments in leaves and not just green is________ Go to Socrative on your cell phone. My room # is BRADYAPBIO 1. What leaf structure allows for gas exchange? a. chloroplast c. inner membrane b. stomata d. chlorophyll 2. What is the source of oxygen that is released from plant cells as a result of photosynthesis? a. carbon dioxide c. glucose b. ATP d. water 3. Based on the absorption spectrum in your notes, what wavelength of light is absorbed the most during photosynthesis? a. 700 nm c. 450 nm b. 600 nm d. 550 nm 4. Carbon dioxide becomes ______ in photosynthesis, forming glucose. a. reduced c. charged b. oxidized d. broken down 5. Photosynthesis converts _______ energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. a. light c. electrical b. chemical d. thermal IV. How pigments react to light energy SO . . … What’s The Point? EHeat E- 1. Photosynthesis captures the energy from the excited electron to make ATP Fluorescence Light ATP EGreen Light ReflectedPigment 2. The ATP is then used to build Glucose V. The Light Dependent Reactions Chloroplast Thylakoid Grana Stroma Stroma Light H+ Light H+ E- H+ Fd E- Thylakoid E- Pq NADPH PC PS I NADP H2O PS II H+ Pump Reductase (P700) Thylakoid O2 (P680) Proton Motive Force H+ H+ space H+ Chemiosomosis H+ H+ Stroma ADP ADP Photophosphorylation 1. Cyclic 2. Non-Cyclic ADP ATP Synthase ATP Calvin Cycle Cyclic verses Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation Non-Cyclic 1. Electron from water never “recycles” 2. Electron used to make NADPH 3. Requires Photosystem I and II 4. Takes place when plenty of H+ and ATP available (H20 is plentiful) Cyclic 1. Electron recycles 2. Electron used to fill the empty electron hole 3. Only uses Photosystem I 4. Makes ATP even though H2O is unavailable VI. The Calvin Cycle- Building Compounds 1 Carbon at a Time Making the numbers balance CO2 (3 CO2 molecules enter) (3 - 6C Unstable compounds) Rubisco (Ribulose BiPhosphate Carboxylase) (3 - 5C RubBP) Unstable 6 Carbon compound(6 - 3C Stable Carbon dioxide acceptor 5c RuBP Ribulose BiPhosphate compounds) (2) PGA Phase 1 Carbon Fixation 3c ATP ADP ADP Phase 3 Regeneration of CO2 Acceptor ATP Rearrangement of carbons Phase 2 Reduction (2) 3c (2) PGAL/G3P PGAL NADPH NADP Pi 3c (5 - 3C Stable compounds) Photosynthesis fills the PGAL Bucket for many metabolic products 3c Krebs Cycle 1. Amino Acids - Proteins Bucket O’ PGAL 2. Glycerol & Fatty Acids- Lipids 2PGAL = C6H12O6 How Photosystems Harvest Light Slide 11 Plasmodesmata Note: All C4 plants are easy to identify by the presence of the unique Bundle Sheaths and Mesophyll cells Slide 13 Photosystem II sends electrons to a higher energy level Slide 9 Electron Acceptor Light Reaction Center 1. Pq (Plastiquione) 2. FD (Ferredoxin) EE- Chlorophyll a E- E- E- EE- E- Photosystem Donates the electron How does chlorophyll “a” refill its electrons? Antenna Pigments 1. Chlorophyll “b” 2. Carotene 3. Xanthophyll The Structure of Chlorophyll On membrane surface Embedded in the membrane Metal that allows transfer of electrons Slide 11 Slide 8 Slide 8 Slide 7 SLIDE 11 The Metabolic Possibilities of PGAL Slide 11 Cell Respiration (Glycolysis) Vs. Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle) PGAL PGAL H H ATP 1,3-Biphosphoglycerate PGA Pyruvic Acid ATP 1,3-Biphosphoglycerate 2PGA Unstable 6 Carbon CO2 + Ribulose Bi Phosphate Slide 11 Slide 9