* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrodes for stimulation
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Syncope (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Transcranial direct-current stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Functional electrical stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
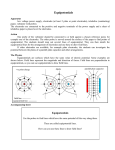
ELECTRODES FOR STIMULATION Cardiac Pacemakers and Defibrillators The heart is a natural example of a critical Bioelectromagnetic system. An electrocardiogram (ECG), which is used to diagnose the control signals of the heart, is a mapping of the electrical voltages produced by the heart on the surface of the body. External electrodes are placed on the body’s surface to receive these electrical signals. As with any voltage, the surface potentials must be measured relative to a reference (or ground) electrode. Cont… Cardiac electrical signals sometimes malfunction. During a heart attack, for instance, the heart may go into fibrillation where the electrical signals become confused and don not progress the heart in the correct order, thus not allowing the heart contract properly for pumping of blood. Then an external defibrillator may be used. The defibrillator uses a pair of electrodes (paddles) that are placed of the chest. One of these electrodes is ground , and the other has a large voltage, producing a shock across the heart that attempts to restart the normal electrical activity of heart. Cont… Defibrillators can also be implanted internal to the body. In that case, the battery pack is placed in the shoulder or chest cavity of the patient.. The metal case (usually titanium) of the battery pack is left in contact with body and a metal wire is surgically attached near an electrically sensitive point on the heart. A very similar device can be used for cardiac pacing. A pacemaker typically works continuously, controlling most if not all of the heart’s beats, where as a defibrillator typically works only occasionally when needed Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) have been used for a number of medical applications. Electrodes on the surface of the body are most often used for these applications, although internal electrodes can be used in isolated applications. It is used to stimulate the body for pain control, bone and tissue healing, and nerve stimulation. Pulsed electromagnetic fields have been found to be highly effective for healing fractures and soft tissue injuries, particularly those that do not respond to ordinary healing methods. Cont… Another application of pulsed electromagnetic fields is for controlling pain in the knee, back and shoulder. Pulsed electromagnetic fields are also used for a wide variety of needleless drug delivery applications. Direct Nerve Stimulation An electrodes used for neural stimulation. Deep brain stimulators for treatment of Parkinson’s disease currently use a device very similar to a cardiac pacemaker. A battery pack is embedded in the shoulder, and a wire lead is run up the neck to the brain, where an implanted can stimulate the brain to relieve tremors. Both external electrodes and invasive needle electrodes are used for stimulation of nerves and muscles for therapy and diagnostic purpose. Cont… Stimulation of the optical nerve for retinal implants and the auditory nerve for cochlear implants, as well as bypassing a damaged spinal cord, have all been demonstrated in the laboratory Treatment of urinary, rectal, and erectile dysfunction has also been proposed using implantable neural stimulators. Ablation Ablation refers to using large amounts of localized heat (burning) to treat medical conditions. Cardiac ablation uses this localized heat to destroy illconducting pathways in heart muscles. In coronary arteries, it is used to break up plaque and clear the arteries. All ablation applications require very precise control of the localized heating.