* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Batteries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
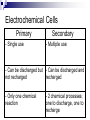
Cells and Batteries A cell is a unit which includes two electrodes and one electrolyte. In your fruit battery the electrodes were the metal strips and the electrolyte was the juice in the fruit. When two or more cells are connected together, the combination is called a cell. Dry cells are connected in series to obtain a larger amount of energy and a higher electric potential (voltage). Batteries are made of a serious of cells. A 9 volt, has 6 cells that produced 1.5V each (1.5V x 6 cells = 9V). When dry cells are connected in series, the electric potential (voltage) increases by 1.5V each time a new cell is added to the set of dry cells. The amount of energy in the battery increases each time a new dry cell is added. Electrochemical Cells Primary - Single use Secondary - Multiple use - Can be discharged but - Can be discharged and not recharged recharged - Only one chemical reaction - 2 chemical processes; one to discharge, one to recharge List advantages and disadvantages of each Primary Secondary Advantage: Advantage: - Has only one chemical reaction - Can be used multiple times Disadvantage: Disadvantage: - Can only be used once - Has 2 chemical processes