* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 5 PLANET EARTH
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
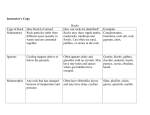
UNIT 5 PLANET EARTH TOPIC 1 MINERALS GRADE 7 Rock- made up of minerals Crust- thin outside layer of Earth Element- a pure substance Lustre- “shininess” Streak- the colour left when a mineral is rubbed across a piece of unglazed porcelain Cleavage- breaks along smooth, flat surfaces Fracture- breaks with rough or jagged edges TOPIC 2 ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE Igneous rock- formed from hot magma or lava Magma- melted rock found in earth Intrusive rock- rock formed very deep and slowly in Earth’s crust Lava- when magma breaks through Earth’s crust from an volcanic eruption Extrusive rock- rock formed when lava cools on Earth’s surface Sedimentary rock- formed from sediment (loose bits of rock, minerals, and plant and animal remains) Sediment- loose bits of rock, minerals and plant and animal remains Stratification- visible layers in rocks that are packed and cemented together Compaction- squeezing or compressing together Cementation- natural forming cement that sticks rocks together (made from minerals dissolved by water as it soaks through the rock Metamorphic- changed form of rock, formed from high pressure and heat Parent rock- the type of rock that changed or the original or first rock ***ROCK CYCLE SEE FIGURE 5.19 PAGE 368*** Compost- dead plant matter Humus- dark rich coloured soil Fertile soil- can supply nutrients for plant growth Leaching- the removal of soil materials dissolved in water TOPIC 3 EROSION Erosion- movement of rock and mineral grains from one place to another Weathering- broken down or worn away ( the movement of rock and minerals) Mechanical weathering- physical breaking up by wind, water, or gravity Chemical weathering- breaking up by the effects of chemical reaction Biological weathering- physical or chemical break down by li8ving organisms such as plants, animals, bacteria, or fungi Abrasion- wearing down of rocks by wind, ice, waves, and running water Frost wedging- freeze-frost cycle Sedimentation- process for building up rock TOPIC 4 THE MOVING CRUST Mantle- found under Earth’s crust Sonar- sound wave technology Plates- pieces of the Earth’s crust Converging plates- two plates pushing together Diverging plates- two plates pulling apart Convection current- flow resulting from the rise of warm materials and the sinking of cool Subduction zones- when two plates collide or converge and one is shoved under the other TOPIC 5 EARTHQUAKES Seismograph- instruments used to measure earthquakes Bedrock- the solid rock that lies beneath the soil and looser rocks Richter scale- method of measurement to describe the strength of earthquakes Seismic waves- ground shaking movement Aftershocks- smaller earthquakes after the large one Primary or P waves- 1st waves, travel the fastest, travel through solid, liquid, and gases Secondary of S waves- travel slower, travel through solids Surface waves- slowest, cause most damage Focus- place where earthquake begins Epicentre- surface location directly above the focus Fault- where rock breaks suddenly because of pressure ***TYPES OF FAULTS FIGURE 5.54 PAGE 403*** TOPIC 6 VOLCANOES Vents- openings Dormant- not active Ring of Fire- circle of volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean TOPIC 7 MOUNTAINS Anticline- top part of folded mountain Syncline- bottom part of folded mountain Thrust faulting- low angle faulting of rock Fault block mountains- mountains formed by the process of thrust faulting Complex mountains- mountains formed by the combined processes of folding and faulting TOPIC 8 FOSSILS Petrified- a rock like substance Carbonaceous film- a type of fossil found in sedimentary rock when organic materials are compressed Original remains- fossils Trace fossils- evidence of animal activity TOPIC 9 GEOGRAPHIC TIME Principle of superposition- geological theory older rock will be layered on bottom Strata- sedimentary layers of rock Relative dating- a way scientists determine the relative age of rocks by examining their position Index fossil- fossil that can be uses to determine the age of material in which it is found Half life- the amount of time a radioactive substance takes to be reduced by one half Radiocarbon dating- type of radiometric dating, to find out when recent events in Earth’s history occurred Eons- the largest division of time on the geological scale Eras- one of the four longest subdivisions of an era Periods- on the geological scale subdivision of and era Precambrian- the first 4 billion years (vast, with little fossil evidence) Rodinia- earliest supercontinent THREE ERA’S Paleozoic Era- ancient life Mesozoic Era- middle life Cenozoic Era- recent life Pangaea- second supercontinent Laurasia- northern portion of Pangaea Gondwanaland- southern portion of Pangaea TOPIC 10 FOSSIL FUELS Petroleum- naturally occurring mixture of hydrocarbons such as bitumen, coal, oil, gas Fossil fuels- soft parts of animals and plants that are transformed into solid, liquid, or gas hydrocarbons Bitumen- heavy solid form of petroleum