* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Instructor Copy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
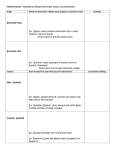
Instructor’s Copy Rocks How can rocks be identified? Rocks may show ripple marks, mudcracks, raindrops and fossils. Can often see sand, pebbles, or stones in the rock. Type of Rock Sedimentary How Rock Is Formed Rock particles settle from different areas (usually in water) and are cemented together. Examples Conglomerates, limestone, rock salt, rock gypsum, chert, Igneous Cooling magma (above or below the ground). Often appears shiny and glasslike with no crystals. May have tiny holes and spaces where gas bubbles have escaped. Granite, diorite, gabbro, rhyolite, andesite, basalt, pumice, scoria, obsidian, basalt Metamorphic Any rock that has changed because of temperature and pressure. Often have ribbonlike layers and may have shiny crystals. Slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, quartzite, marble