* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1, Changes to Earth`s Surface
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
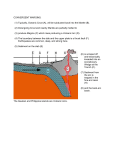
Chapter 1, Changes to Earth’s Surface Lesson 1 Landforms – physical features on the Earth’s surface Weathering – process of breaking rock into silt, sand, clay, and sediment Erosion – process of moving sediment from one place to another Deposition – process of dropping, or depositing, sediment in a new location Mass movement – downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity Lesson 2 Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – mountain formed by lava and ash Earthquake – shaking of the ground caused by the sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust Faults – places where pieces of the crust move Lesson 3 Continental drift – theory of how Earth’s continents move over its surface Pangea – theory that 225 million years ago the Earth was joined together in one supercontinent Fossils – remains or traces of past life found in some rocks