* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Today`s Warm-Up Friday, January 10
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
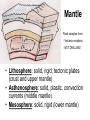
Today’s Warm-Up Friday, January 10 • Write What You Know! Write as much as you can for five minutes on the prompt below, try for at least 3-4 complete sentences. • Astronomy Throwback! Do other planets in our solar system also have layered atmospheres and layered interiors like the Earth does? Why? Why is the Earth’s core made of metal, and the mantle and crust made of different types of rock? Why isn’t everything the same inside the planet? Earth’s Interior Section 1.1 Exploring Inside Earth • How do we know about the Earth’s interior structure? • Direct Evidence: Rock Samples – From drilling, volcanoes, and tectonic movement • Indirect Evidence: Seismic Waves – Energy waves from earthquakes, change path and speed as they move through the Earth. Why? – Waves travel differently through different materials Journey to the Center of the Earth • As you go deeper into the Earth . . . – Temperature increases, it gets hotter! – Pressure increases – Material becomes more dense – Materials change from lighter rock to heavier rock to metal – Lots of water trapped inside Earth! Crust • Crust is solid, rigid rock – Breaks under pressure – Broken into many tectonic plates Crust • How far down have we gone? – Deepest bore hole (drill) 12 km down – Deepest cave discovered 3 km down – Border between crust and mantle • 5 km average oceanic crust • 70 km average under mountains Mantle Rock samples from: - Volcanic eruptions - NOT DRILLING! • Lithosphere: solid, rigid, tectonic plates (crust and upper mantle) • Asthenosphere: solid, plastic, convection currents (middle mantle) • Mesosphere: solid, rigid (lower mantle) Core • Outer Core: liquid metal (nickel & iron) • Inner Core: solid metal (nickel & iron) • Why is Inner Core solid not liquid? – PRESSURE! Magnetic Field Magnetic Field • The Earth rotates to the east – Outer core rotates west, inner core rotates east, in the opposite direction! – Speed of core’s rotation is faster than the planets, and changes over time! • This generates our magnetic field, or magnetosphere – Protects us against solar wind! Creates auroras at the poles! – What would happen if the entire core cooled down into solid metal and stopped rotating?