* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reinforcement learning and human behavior
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence for video surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual control theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
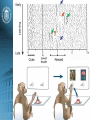
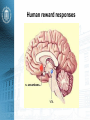
Reinforcement learning and human behavior Hanan Shteingart and Yonatan Loewenstein MTAT.03.292 Seminar in Computational Neuroscience Zurab Bzhalava Introduction • Operant Learning • Dominant computational approach to model operant learning is model-free RL • Human behavior is far more complex • Remaining Challenges Reinforcement Learning RL: A class of learning problems in which an agent interacts with an unfamiliar, dynamic and stochastic environment Goal: Learn a policy to maximize some measure of long-term reward Markov Decision Process • • • • A (finite) set of states S A (finite) set of actions A Transition Model: T(s, a, s’) = P(s’ | a ,s) Reward Function: R(s) • ᵧ is a discount factor ᵧ ∈ [0; 1] • Policy π • Optimal policy π* Markov Decision Process Bellman equation: Biological Algorithms • Behavioral control • Evaluate the world quickly • Choose appropriate behavior based on those valuations midbrain's dopamine neurons • Central role in guiding our behavior and thoughts • Valuation of our world – Value of money – Other human being • • • • • Major role in decision-making Reward-dependent learning Malfunction in mental illness Related to Parkinson's disease. Schizophrenia Reinforcement signals define an agent's goals 1. organism is in state X an receives reward information; 2. organism queries stored value of state X; 3. organism updates stored value of state X based on current reward information; 4. organism selects action based on stored policy 5. organism transitions to state Y and receives reward information. The reward-prediction error hypothesis Difference between the experienced predicted “reward” of an event and • Neurons of the ventral tegmental area • phasic activity changes encode a 'prediction error about summed future reward' prediction-error signal encoded in dopamine neuron firing. Value binding Human reward responses • • • • • • Orbitofrontal Cortex (OFC) Amygdala (Amyg) Nucleus Accumbens Sublenticular extended amygdala Hypothalamus (Hyp) Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) Human reward responses Model-based RL vs Model-free RL • goal-directed vs habitual behaviors • Implemented by two anatomically distinct systems (subject of debate) • Some findings suggest: – Medial striatum is more engaged during planning – Lateral striatum is more engaged during choices in extensively trained tasks Model-based RL vs Model-free RL (b) Model-free RL (c) Model-based RL Human subjects in exhibited a mixture of both effects. Challenges in relating human behavior to RL algorithms • Humans tend to alternate rather than repeat an action after receiving a positively surprising payoff • Tremendous heterogeneity in reports on human operant learning • Probability matching or not Heterogeneity in world model Questions? Learning the world model Questions? Reference List: • Reinforcement learning and human behavior Hanan Shteingart and Yonatan Loewenstein • The ubiquity of model-based reinforcement learning Bradley B Doll Dylan A Simon3 and Nathaniel D Daw • Computational roles for dopamine in behavioral control P. Read Montague1,2, Steven E. Hyman3 & Jonathan D. Cohen4,5