* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The immune system
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
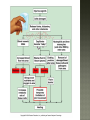
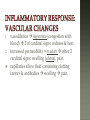
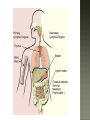
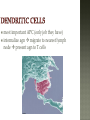
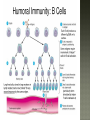
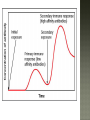
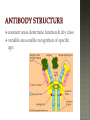
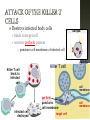
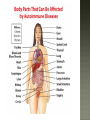
Honors Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 21 nonspecific defense that is active immediately upon infection found in all animals & plants includes: outer covering skin or shell chemical secretions @ openings to interior of body skin, mucous membranes & their secretions highly effective barriers…unless not intact epidermis with thick keratinized layers of cells blocks most microorganisms keratin resistant to most bacterial enzymes & toxins intact mucosae just as protective 1. Acid acidic pH inhibits bacterial growth (bacteriostatic) 2. Enzymes Lysozyme in saliva, tears, sputum bacteriocidal gastric enzymes also bacteriocidal 3. Mucin + water sticky lining of digestive & respiratory passages: traps pathogens 4. Defensins: broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides secreted by mucous membranes & skin 5. Other: lipids in sebum & dermicidin in eccrine sweat toxic to bacteria 1. Phagocytes: Neutrophils become phagocytic when find infectious material Fixed & Wandering Macrophages from monocytes 2. Natural Killer Cells in lymph phagocyte must adhere to pathogen in order to ingest it bacteria with external capsules elude capture Opsonins: proteins released by immune cells that coats the capsules (opsonization) phagocytes can capture them nonspecific killers of any cell w/out “self” cell surface markers travel through body patrolling for: virus-infected cell cancer cells Not phagocytic induce target cell apoptosis secrete potent chemicals that enhance inflammatory response triggered when tissues injured by: physical trauma 2. intense heat irritating 3. chemicals 4. infection by viruses, fungi, or bacteria 1. beneficial 1. 2. 3. 4. effects: prevents spread of damaging agents to nearby tissues diposes of cell debris & pathogens alerts adaptive immune response sets stage for repair *ultimate goal: clear injured area of pathogens, dead tissue cells, other debris so tissue can be repaired 1. 2. 3. 4. Redness Heat Swelling Pain 1st step: “chemical alarm” chemicals released by: injured or stressed cells immune cells mast cells histamine macrophages recognize type of invader using surface receptors called TLRs and release specific chemical in response triggers release of cytokines other chemicals released: kinins prostaglandeins complement 1. 2. vasodilation hyperemia (congestion with blood) 2 of cardinal signs: redness & heat increased permeability = exudate other 2 cardinal signs: swelling (edema), pain capillaries allow fluid containing clotting factors & antibodies swelling pain macrophages predominant cell cleaning up cell debris @ sites of prolonged or chronic inflammation pus: mixture of dead or dying neutrophils, damaged or dead tissue cells, living & dead pathogens if inflammatory response has failed to clear area collagen fibers may be laid down walling off area abscess: may require surgical drainage to heal 1. Interferons secreted by cells in response to viral invasion not viral specific help nearby cells make proteins that interfere with viral replication 2. Complement provides major mechanism for destroying foreign substances in body releases inflammatory chemicals lyses & kills certain bacteria abnormally high body temperature pyrogens: chemicals released by neutrophils & macrophages alters thermostat in hypothalamus adaptive response that benefits body: 1. liver & spleen sequester iron & zinc making them less available to support bacterial growth 2. increases metabolic rate of tissue cells in general https://www.khanacademy.org/science/hea lth-and-medicine/human-anatomy-andphysiology/introduction-toimmunology/v/inflammatory-response body‘s built -in specific defense system 3 features: 1. Specific 2. Systemic 3. Memory 2 parts 1. Humoral or antibody-mediated immunity B Cells 2.Cellular or cell-mediated immunity T Cells 1. complete antigens 2. incomplete antigens Functions: 1. 2. Immunogenicity: ability to elicit certain lymphocytes to proliferate (multiply) Reactivity: ability to react with activated lymphocytes & the antibodies released B lymphocytes T lymphocytes make antibodies cellular immunity humoral mature in thymus immunity 1. Immunocompetence mature in bone ability of immune cells marrow to recognize (by binding) to specific agns; recognition implies presence of plasma membrane receptors 2. Self-tolerance APCs engulf agns present fragments of them onto their cell-surface markers major types: 1. Dendritic cells 2. Macrophages 3. B cells most important APC (only job they have) internalize agn migrate to nearest lymph node present agn to T cells present agns to T cells in order to be activated by effector T cells release chemicals that in turn activate the macrophage increases their phagocytic activity do not activate naïve T cells like dendritic cells or macrophages only present to T helper cells in order to get help for their own activation once activated, most of the clone members become effector cells = plasma cells plasma cells secrete antibodies rest become memory cells http://web.biosci.utexas.edu/psaxena/Micro biologyAnimations/Animations/HumoralIm munity/micro_humoral.swf Memory cells capable of mounting a rapid attack against the same antigen in any later encounters (secondary immune response) Memory B cells provide humoral immunological memory http://web.biosci.utexas.edu/psaxena/Micro biologyAnimations/Animations/HumoralIm munity/micro_humoral.swf acquired during 1st exposure to agn: Infection Vaccination provides memory acquired Active through injection of abys into body passage of abys from mother fetus in utero passage of abys to newborn in breastmilk *NO MEMORY Passive Immune system exposed to harmless version of pathogen triggers active immunity stimulates immune system to produce antibodies to invader rapid response if future exposure Most successful against viral diseases 1914 – 1995 April 12, 1955 Developed first vaccine against polio attacks motor neurons Albert Sabin 1962 oral vaccine 4 polypeptide chains 2 heavy chains 2 light chains held together by disulfide bonds constant areas determine function & aby class variable area enable recognition of specific agn 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ig M: 1st aby secreted from plasma cell during 1◦ response, potent agglutinator Ig A: found in body secretions: saliva, sweat, milk, blocks attachment of agns to mucous membranes Ig D: functions as B cell membrane agn receptor Ig G: most #’s in plasma, main aby of 1◦ & 2◦ responses, only 1 to cross placenta Ig E: binds to mast cells & basophils release histamine, levels rise during allergic rx or chronic parasitic infections of GI tract http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072507470/stude nt_view0/chapter22/animation__the_immune_response.ht ml pure preparations (a clone) of a single aby type useful in diagnostic tests 1. 2. 3. pregnancy STDs Hepatitis treating some types of cancer Leukemia Lymphomas You need trained assassins to kill off these infected cells! T Attack of the Killer T cells! 2007-2008 agn presentation to T cells provokes cellular immune response 2 major populations of T cells (based on which of 2 surface proteins a mature T cell displays:; both memory cells: 1. CD4 = helper T cells: TH activate B cells, macrophages direct adaptive immunity (does not happen w/out TH CD8= cytotoxic T cells: TC 2. destroy any cell in body that has anything foreign in it infected cell killer T cell or activated macrophage helper T cell helper T cell stimulate B cells & antibodies helper T cell Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y helper T cell Y Y Y interleukin 1 activate killer T cells Y helper T cell Destroys infected body cells binds to target cell secretes perforin protein punctures cell membrane of infected cell Killer T cell binds to infected cell infected cell destroyed Killer T cell vesicle cell membrane perforin punctures cell membrane target cell cell membrane http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072507470/st udent_view0/chapter22/animation__tcell_dependent_antigens__quiz_2_.html skin free antigens in blood humoral response Y Y antibodies Y Y Y Y memory B cells Y Y Y Y Y macrophages (APC) helper T cells B cells plasma B cells pathogen invasion antigen exposure skin antigens on infected cells cellular response T cells memory T cells cytotoxic T cells cell-mediated responses reject grafts & foreign transplants unless the recipient is immunosuppressed infections are major complications SCID 1. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency group of genetic disorders deficit of functioning T and B cells untreated:fatal tx:bone marrow transplant acquired immunodeficiencies 1.Hodkins lymphoma 2. AIDS Human Immunodeficiency Virus virus infects helper T cells helper T cells don’t activate rest of immune system: T cells & B cells also destroy T cells Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome infections by opportunistic diseases death usually from other infections pneumonia, cancer occurs when the body regards its own tissues as foreign & mounts an immune attack against it Rheumatoid arthritis Graves disease Hashimoto’s thyroiditis Multiple sclerosis Celiac disease Lupus (SLE) abnormal reaction to otherwise harmless agn immediate hypersensitivity 1. allergies/ Ig E aby 2. subacute hypersensitivity: abys & complement 3. delayed hypersentsitivity: cell-mediated 4 attributes that characterize the immune system as a whole specificity diversity react to millions of antigens memory antigen-antibody specificity rapid 2° response ability to distinguish self vs. non-self maturation & training process to reduce auto-immune disease