* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biological Significance of Lipids
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
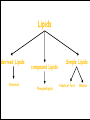
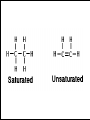
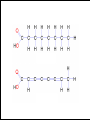
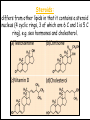
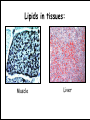
Lipids in cells & Tissues Lipids :are macromolecules composed of C, H and O, and other atoms as Phosphor. They are water-insoluble but dissolve in organic solvents as alcohol and acetone. Biological Significance of Lipids: 1- Component of cellular membranes. 2- Source of energy and contains more energy than carbohydrates. 3- Some hormones are lipid-derivatives. 4- Work as heat insulator, and shock absorbent. Fatty acids + Alcohols = Lipids Lipids derived Lipids Steroids compound Lipids Phospholipids Simple Lipids Neutral fats Waxes Neutral fats: Most lipids in cell and in general are neutral fats. They are composed of 1 molecule of glycerol and 3 molecules of fatty acids. Neutral fats can be either saturated fats like butter, or unsaturated like oils. Waxes: similar to neutral fats structure but instead of glycerol they contains other larger alcohols. Phospholipids: Has 1 phosphate group (PO4) instead of one fatty acid. Found in all cells as component of cellular membranes Steroids: differs from other lipids in that it contains a steroid nucleus (4 cyclic rings, 3 of which are 6 C and 1 is 5 C ring). e.g. sex hormones and cholesterol. Lipids in tissues: Muscle Liver Detection of Cholesterol in samples: milk, butter, margarine, olive and corn oil 1- Mark 6 tubes from 1-6, to each tube add 0.5 ml of acidic potassium sulfate KHSO4. Add 5 drops of each sample to each tube, then add 2.5 ml of KHSO4 Heat over flame for few minutes. 2- Mark 6 new tubes from 1-6, to each tube add 2 ml of sample + 1 ml chloroform + 1 ml of acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O + 2 ml of conc. Sulfuric acid (very carefully).