* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Review KEY
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
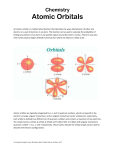
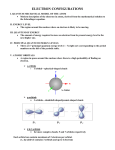
CP Chem Ms. Lummis Unit 2 Exam Review 1 Worksheet KEY Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on a metal. Quantum – minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. Photon – particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. Heisenberg uncertainty principle – it is impossible to determine at the same time both the position and the velocity of an electron or any other very small particle. Quantum theory – describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles. Orbital – the region of space where it is most likely to find an electron (90%) Principal Quantum number(n) - the main energy level. Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l) - the energy sublevel. It indicates the shape of the orbital, s, p, d, f. Magnetic Quantum Number (m) - indicates the orientation of the orbital. Magnetic Spin Quantum Number(s) - fundamental spin state of an electron in an orbital. Aufbau Principle – the electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it. Pauli Exclusion Principle – no 2 electrons in the same atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. Hund’s Rule – orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron. All electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin state. Directions: use the diagram below of the Bohr model to help answer the following questions: 1. Which letters correspond to energy levels? A, B, D 2. What type of particles are allowed to exist in these energy levels? electrons 3. Which letter represents an orbit with the lowest energy state? A 4. Which letter represents a point where electrons could not reside, according to the Bohr model. C 5. Explain what these orbitals represent, according to quantum theory. Principal quantum number. Fill in the following table: Sublevel # of Orbitals Max # of Electrons s (0) Description of shape sphere 1 2 p (1) dumbbell 3 6 d (2) cloverleaf 5 10 f (3) complex 7 14 Directions: Answer the following questions regarding an atom with the electron configuration 1s22s22p6. (Note: this is an example) How many electrons are present in this atom? 10 What element is this atom? Neon How many of this atom’s p orbitals are completely filled? 3 How many unpaired electrons are there in this atom? 0 How many inner-shell electrons does this atom have? 2 Write the electron configurations and Noble gas notation of the following elements: Li 1s22s1 [He] 2s1 Mg 1s22s22p63s2 [Ne] 3s2 As 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3 [Ar] 4s23d104p3 Mo 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d4 Ba 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s2 S 1s22s22p63s23p4 K 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 [Kr] 5s24d4 [Xe] 6s2 [Ne] 3s23p4 [Ar] 4s1 Write the orbital notations for Li, S, K and As: DO NOT DO THIS ONE _____+1/2 ___ -1/2__________ The spin quantum numbers are what 2 numbers? _____2_______ If you are in the second energy level, what orbitals are there? ___4:____s__p__d___f__ On the 4th energy level, how many sublevels are there? ___________6____________ How many electrons can be found in the p-orbitals? _________14____________ How many electrons are found in the f-orbitals? _____s___p___d____f_____ If you are in the fifth energy level, what orbitals are there? _____spherical___________ What is the shape of the s-orbital? _________s_________Which orbital can be found at every energy level? _______dumbbell_________ What shape are the p-orbitals? Draw the arrow diagram: See your notes