* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Orbitals and quantum numbers
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen-vacancy center wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
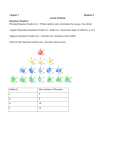
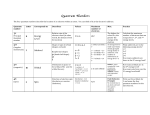
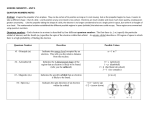
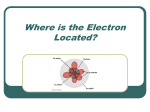
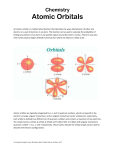
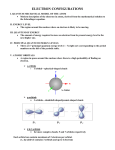
Quantum Numbers •Four Quantum Numbers: •Specify the “address” of each electron in an atom UPPER LEVEL Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Quantum Numbers •Principal ( n ) •Angular Momentum ( l ) •Magnetic ( ml ) •Spin ( ms ) 1. Principal Quantum Number (n) • Energy level 1s • Size of the orbital • n2 = # of orbitals 2s in the energy level 3s Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem 1s orbital imagined as “onion” Concentric spherical shells Copyright © 2006 Pearson Benjamin Cummings. All rights reserved. Angular Momentum (l) •Defines the shape of the orbital. • Energy sublevel •Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n − 1. •We use letters to describe the different values of l and, therefore, the shapes and types of orbitals. Value of l 0 1 2 3 Type of orbital s p d f Magnetic Quantum Number, ml •Describes the three-dimensional orientation of the orbital. •Values are integers ranging from -l to l: −l ≤ ml ≤ l. •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. l=0 (s), m=0 l=1 (p), m=-1,0,1 l=2 (d), m=-2,-1,0,+1,+2 l=3 (f), m=-3,-2,-1,0,+1,+2,+3 Energy Levels, Orbitals, Electrons Energy Level (n) Orbital type in the energy level (types = n) Number of Orbitals (m) Number of Electrons Number of electrons per Energy level (2n2) 1 s 1 2 2 2 s p 1 3 2 6 8 3 s p d 1 3 5 2 6 10 18 4 s p d f 1 3 5 7 2 6 10 14 32 A maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital Electron Spin Electron spin describes the behavior (direction of spin) of an electron within a magnetic field, which affects its energy. Possibilities for electron spin: 1 2 1 2 Indicates two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital.