* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
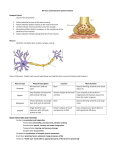
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue BIO 210 Lab Instructor: Dr. Rebecca Clarke Nervous System Includes all neural tissue in the body Organs Brain and spinal cord Sensory receptors Nerves Anatomical Divisions of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) • • Brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) • All other neural tissue outside CNS, i.e., receptors, nerves, ganglia Functions of the CNS Acts as control center for nervous system Integrates, processes, coordinates: Sensory data: Convey info about conditions inside/outside body Motor commands: Control/adjust activities of peripheral organs, e.g., skeletal muscles Higher functions of brain: Intelligence, memory, learning, emotion Provides short-term control over activities of other systems Functions of the PNS Links CNS with other systems and with sense organs Delivers sensory information from receptors to CNS Carries motor commands from CNS to peripheral tissues and systems Neural Tissue Consists of 2 kinds of cells: Neurons: Send and receive signals Perform all communication, information processing, and control functions of NS Neuroglia (glial cells): Support and protect neurons Preserve physical and biochemical structure of neural tissue Essential to survival and function of neurons Structure of a Neuron Neuron: basic functional unit of nervous system Figure 12–1 Multipolar Neuron Common in the CNS Large cell body (soma): = perikaryon + nucleus Several short, branched dendrites Single, long axon Major Organelles of the Cell Body Large nucleus with nucleolus Cytoplasm (perikaryon) Mitochondria (produce energy) RER and ribosomes (produce neurotransmitters) Cytoskeleton (supports dendrites and axon) LACK centrioles Can’t divide Nissl Bodies Dense areas of RER and ribosomes Make neural tissue appear gray Neuron cell body = gray matter Dendrites Highly branched processes Extend from cell body Dendritic spines: Many fine processes Receive information from synaptic end bulbs/axonal terminals of axons of other neurons 80–90% of neuron surface area Axon Long process that extends from cell body Carries electrical signal (action potential) away from cell body Axon structure is critical to function Structures of the Axon (1 of 3) Axoplasm: Cytoplasm of axon Axolemma: Specialized cell membrane Covers axoplasm Structures of the Axon (2 of 3) Axon hillock: Cone-shaped, broad region of cell body Attaches to… Initial segment: Base of axon that attaches to axon hillock of cell body Structures of the Axon (3 of 3) Collaterals: Branches of a single axon Enable axon to communicate with other cells Telodendria: Fine extensions of distal axon Synaptic (axonal) terminals/end bulbs/knobs: Tips of telodendria Myelin/Myelin Sheath Glossy white, multilayer, lipid wrap around axon Insulates axon from contact with extracellular fluid (like insulation on electrical wires) Increases speed of action potential along axon Regions of CNS with many myelinated neurons white matter of CNS Myelin/Myelin Sheath Formed by: Schwann cells (PNS neuroglia) Oligodendrocytes (CNS neuroglia) Schwann Cells Wrap around axons of PNS Myelin sheath (like oligodendrocytes in CNS) Last layer of wrap (outer surface) = neurilemma Loose sheath Contains nucleus and cell organelles Internodes = wrapped areas of axon Nodes (of Ranvier) = gaps between internodes Figure 12–5a Schwann Cells 1 Schwann cell sheaths 1 segment of axon Many Schwann cells sheath entire axon Axons branch at nodes collaterals Oligodendrocytes Wrap around CNS axons Can myelinate portions of several adjacent axons Process different from Schwann cells Schwann cells can myelinate only one segment of a single axon Figure 12–4 Endoneurium Connective tissue layer Surrounds neurilemma of nerve fiber 4 Structural Classifications of Neurons Multipolar neuron Unipolar neuron Bipolar neuron Anaxonic neuron Multipolar Neuron 2 or more dendrites 1 Long axon Most common type in CNS Includes all skeletal muscle motor neurons In somatic nervous system (SNS) Figure 12–3) Unipolar Neuron 1 Long axon Fused dendrite and axon Cell body to one side Found in sensory neurons of PNS Figure 12–3 Bipolar Neuron Small cell 1 Dendrite Branches extensively at distal tip dendritic spines 1 Axon Cell body between axon and dendrite Rare Found in special sense organs, e.g., retina of eye Figure 12–3 Anaxonic Neuron Small All cell processes look alike Found in brain and sense organs Figure 12–3 Functional Classifications of Neurons Sensory Neuron – carries sensory (afferent) information from sensory receptors to the CNS Somatic sensory neurons – monitor outside world and our position in it Visceral sensory neurons – monitor internal conditions Interneuron – between the sensory and motor neurons; information processing Motor Neuron – carries motor (efferent) information from the CNS to the effector Somatic motor neuron – carries info to skeletal muscles Visceral motor neuron – carries info to smooth m., cardiac m., glands, and adipose tissue Neuroglia Supporting cells Half the volume of the nervous system Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS Neuroglia of the CNS Ependymal cells Microglia Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Neuroglia of the CNS: Ependymal Cells Columnar epithelial cells Form ependyma Line fluid (CSF)-filled cavities in: Spinal cord (central canal) Brain (ventricles) Have slender processes on “nonpassageway” side of cell Assist in: Producing, circulating and monitoring composition of CSF Figure 12–4 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Surrounds: Brain Spinal cord Protective cushion Transports dissolved gases, nutrients, wastes, etc. Neuroglia of the CNS: Microglia Smallest, rarest neuroglia in CNS Many fine-branched processes Phagocytic macrophage Migrates through neural tissue; wandering police force/janitorial service Cleans up cellular debris, waste products, pathogens Figure 12–4 Neuroglia of the CNS: Astrocytes Star-shaped Largest and most numerous neuroglia in CNS Have “feet” on end of many processes Wide range of functions Figure 12–4 Functions of Astrocytes Maintain blood-brain barrier “Feet” extensions wrap around capillaries Create 3-D framework for CNS Repair damaged neural tissue Structural repairs that stabilize tissue/prevent further injury Guide neuron development in embryonic brain Control interstitial environment Regulate ion, nutrient, dissolved gas concentrations and transport Control blood flow through capillaries Absorb and recycle NTs Neuroglia of the CNS: Oligodendrocytes Smaller cell body Fewer processes Processes Contact other neuron cell bodies Wrap around axons to form myelin sheath myelinated axon Many oligodendrocytes on each axon Each oligodendrocyte myelinates segments of several axons Figure 12–4 Neuroglia of the PNS Schwann cells Satellite cells Neuroglia of the PNS: Schwann Cells Wrap around peripheral axons of PNS Myelin sheath (like oligodendrocytes in CNS) Figure 12–5a Neuroglia of the PNS: Satellite Cells Surround ganglia (collections of neuron cell bodies) Regulate environment around neurons (like astrocytes in CNS) White Matter and Gray Matter White matter of the CNS Myelinated axons Gray matter of the CNS Neuron cell bodies, unmyelinated axons, and neuroglia Terminology Collection of: CNS PNS Neuron Cell Bodies Nucleus Ganglion Tract Nerve Axons Neural Responses to Injuries Wallerian degeneration Axon distal to injury degenerates Schwann cells Form path for new growth Wrap new axon in myelin Neural Responses to Injuries Nerve Regeneration in CNS Limited by chemicals released by astrocytes that Block growth Produce scar tissue Neural Responses to Injuries Neural Responses to Injuries Neural Responses to Injuries Neural Responses to Injuries