* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon compounds class web14
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
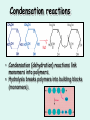
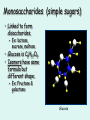
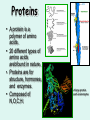
Carbon compounds The chemistry of life Organic molecules • Organic molecules all contain Carbon. • Usually bonded to the elements N, H, O. • CHNOPS are the 6 most common elements in organisms. Amino acid: alanine Why Carbon? • Can form up to 4 bonds. • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. Single bonds Triple bonds Double bonds monomers • Monomers are simple compounds that can be bonded together to form larger ones. • 3 important ones are: – sugars – amino acids – Nitrogen bases sugar Amino acid Nitrogen base macromolecules • Living organisms use 4 types of macromolecules for most cellular functions. – Carbohydrates – Proteins – Lipids – Nucleic Acids Computer generated image of a protein Condensation reactions • Condensation (dehydration) reactions link monomers into polymers. • Hydrolysis breaks polymers into building blocks (monomers). Monosaccharides (simple sugars) • Linked to form disaccharides. – Ex: lactose, sucrose, maltose. • Glucose is C6H12O6. • Isomers have same formula but different shape. – Ex: Fructose & galactose Glucose Carbohydrates • Composed of sugars. • Only: C,H, and O. • Hydrogen to Oxygen ratio is 2:1. • Used for structure and energy storage. • Most common polysaccharides: – Starch – Cellulose which is the most common carbohydrate Plant Cell Walls are made of cellulose Amino acids The structure is a central Carbon atom with a hHydrogen, a carboxyl group, amino group, and variable R group attached Red: carboxyl, Blue: amino polypeptide • A dipeptide is a molecule composed of two amino acids. • Connected by a covalent bond called a peptide bond. • Many amino acids hooked together are called a polypeptide. Four polypeptides of hemoglobin Proteins • A protein is a polymer of amino acids. • 20 different types of amino acids arebfound in nature. • Proteins are for structure, hormones, and enzymes. • Composed of N,O,C,H. A large protein such as an enzyme Nucleic acids • Nucleic acids include: DNA, RNA, and ATP – DNA and RNA are the genetic material for the cell – ATP is an energy storage molecule Lipids • Lipids are fats – Most lipids are hydrophobic/ nonpolar – Lipids are used for storing large amounts of energy – Phospholipids have a polar and nonpolar end • These molecules form the cell membrane Summary • Make a 3 column chart of with a row for each of the 4 macromolecules. Put the name of the macromolecule in the first column, the monomers it is composed of in the second, and the function in the cell in the third.