* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Blood Groups
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
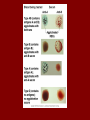
Human Blood Groups Anatomy and Physiology Blood Transfusions • Loss of blood leads to constriction and cell formation • Loss of 15-30% leads to pallor and weakness • Loss of over 30% leads to shock/fatal • Transfusion can restore blood volume – Blood needs to be the proper type Human Blood Groups • RBC membranes have antigen proteins – Cell identification markers – Antibodies recognize the antigens – Cells agglutinate (clump up) • May clog small vessels – Antibodies destroy cells releasing hemoglobin • Leads to kidney damage • ABO and Rh groups the most reactive – Out of 30 antigens ABO Blood Groups • Based on 2 antigens – A and B – One inherited from each parent – AA and A_ type A – BB and B_ type B – AB type AB – Neither type O • One has the opposite antibodies to the antigens on their cells Rh Blood Groups • A different antigen on the RBC – If it is present + not then – • Anti Rh antibodies not automatic – Rh – people have to develop immunity to Rh+ – Second transfusion will cause immune response • Important to Rh- moms with Rh+ fetus – Second + baby could be attacked • Hemolytic disease of the newborn Blood Typing • Important for both donor and recipient • Agglutination test • Eldon Cards – Anti A – Anti B – Anti D(Rh) – Control