* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16 Notes
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
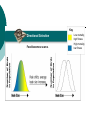
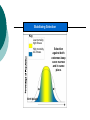
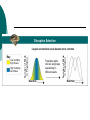
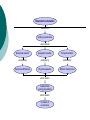
Chapter 16 Notes Spring 2006 Mr. Holmes Darwin’s problem was that he did not understand inheritance. Although Mendel’s work was published during Darwin’s lifetime, the work was not accepted at that time. Phenotype (height) Frequency of Phenotype (copy) All the genes in an organism makes up its total genetic makeup. A gene pool is a combination of all the genetic information of all the members of a particular population. It usually contains two or more alleles (or forms) of a gene. The relative frequency is the number of times an allele appears in a population. Sample Population 48% heterozygous black 16% homozygous black 36% homozygous brown Frequency of Alleles allele for brown fur allele for black fur (copy) The variations in genetic pools are due to mutations and genetic shuffling. Variations would lead to asking the question: Why aren’t all gene pools the same? Crossing over is a process that can lead to variation. A phenotype, or trait, can be due to the result of a single gene or it can be the result of more than one gene working together (polygenic) Key Directional Selection Low mortality, high fitness Food becomes scarce. High mortality, low fitness Stabilizing Selection Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Birth Weight Selection against both extremes keep curve narrow and in same place. Disruptive Selection Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Population splits into two subgroups specializing in different seeds. Beak Size Number of Birds in Population Key Number of Birds in Population Largest and smallest seeds become more common. Beak Size (copy) Genetic drift is the idea that a certain trait disappears or appears in a population by chance and becomes common over time. The founder effect occurs when allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population. Sample of Original Population Descendants Founding Population A Founding Population B (copy) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium states that the allele frequencies in a population remains constant unless one or more factors causes a change. If this happens the situation is said to be at genetic equilibrium. The five conditions of HardyWeinberg equilibrium are: random mating large population no immigration or emigration no mutations no natural selection The formation of a new specie is caused speciation. What causes speciation? The main reason is reproductive isolation behavioral isolation (differences in courtship rituals) geographic isolation (two species separation by geographic barriers) temporal isolation (different times of fertility) Reproductive Isolation results from Isolating mechanisms which include Behavioral isolation Geographic isolation Temporal isolation produced by produced by produced by Behavioral differences Physical separation Different mating times which result in Independently evolving populations which result in Formation of new species