* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download All Optical Networks
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Super-resolution microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Fiber Bragg grating wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
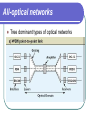
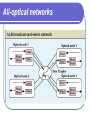
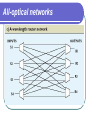
All Optical Networks Samir Chatterjee & Suzanne Pawlowski Presenter: Pengfei Liu Outline To present a general overview of optical networks; To discuss how all-optical networks can be integrated into existing and future broadband network architectures; All-optical Current fiber networks use electronic switching and are therefore limited to electronic speeds of a few gigabits per second. For higher speeds, it is important that the signal remain photonic throughout its path. Such networks, which use optical switching and routing, are called all-optical. Drivers for Optical Networks Internet and Web browsing. Bandwidth requirement *8 More users Response time Graphics and visualization. 2000*2000 12-bit color pixels/frame & 24 frame/sec adds up to 1Gbps Drivers for Optical Networks Medical image access and distribution. Multimedia conferencing. Video: 10-40Mbps HDTV 2-6Mpbs MPEG Broadband services to the home. Optical Transmission System Three basic elements Light Source: infrared lightemitting diodes( LEDs ) or Injection Laser diodes( ILDs ) Transmission medium:singlemode or multimode fiber, ultra-thin glass fiber. Detector: photodiode and phototransistor Optical fiber principles Central core, surrounded by a cladding layer, which is covered by protective jacket ray of light travels through by reflecting along the interface between the two transparent mediums. Optical fiber principles Total Internal Reflection Total internal reflection causes the light to be guided down the fiber. Total internal reflection is directly related to the fact that the refractive index of the cladding( n1 ) is less than the refractive index of the core( n2 ). n1 < n2 Optical Networking Technology Erbium-doped fiber amplifier( EDFA ) Optical signals are regenerated electronically to overcome the attenuation inherent in the silica fiber as well as other losses due to optical components along the line. Optical Networking Technology Wavelength division multiplexing(WDM) All-optical networks Tree dominant types of optical networks All-optical networks All-optical networks Optical Services Network services are provided in the form of layers of various protocols. Optical Services UNI( User Network Interface ) ON( Optical Network ) Circuits (POTS, T-1, SONET), Datagram (IP with its best-effort service) Virtual circuits (frame-relay and ATM). Conclusion Briefly reviewed the state of the technology and possible future directions for fiber-optic networks. There’s still a long way to go. End of Presentation