* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution and Natural Selection
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
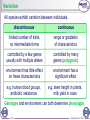
1 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Evolution occurs via natural selection: How to describe natural selection - Individuals within a population show variation due to changes in their DNA (mutations) (state the differences). - Those with features best adapted to an environment survive and reproduce (name the best feature and say why). - These genes/features get passed on to the offspring. - These features become more common in the population The origin of genetic variation Genetic variation is heritable. It is this variation that natural selection acts upon. The causes of genetic variation are: Mutation Sexual recombination deletion, addition or substitution of a nucleotide independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis deletion or translocation of part of a chromosome crossing-over during meiosis aneuploidy – loss or gain of a single chromosome random fertilization. polyploidy – the addition of whole chromosome sets. 4 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Environmental causes of variation Organisms can be affected by their environment. Variation caused by the environment is not heritable, so it is not subject to natural selection. However, the ability of organisms to develop differently in different environments can be genetic. This means organisms can evolve to be flexible. Plants are a good example of this. The number of leaves, growth pattern and size of any individual plant is dependent on the environment, e.g. availability of light and nutrients. 5 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Variation All species exhibit variation between individuals. discontinuous continuous limited number of traits, no intermediate forms range or gradation of characteristics controlled by a few genes usually with multiple alleles controlled by many genes (polygenic) environment has little effect on these characteristics environment has a significant effect e.g. human blood groups, antibiotic resistance e.g. stem height in plants, milk yield in cows Genotype and environment can both determine phenotype. 6 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 What is a gene pool? The gene pool can be defined as: The total information from all the genes and alleles of the breeding individuals in a population at a particular time. The gene pool’s composition changes from one generation to the next as the relative proportions of alleles vary. If there is a consistent change in allele frequency (the proportion of organisms in the population carrying a particular allele) then a population is evolving. 7 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 The Hardy-Weinberg principle 8 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Introducing the Hardy-Weinberg principle The Hardy-Weinberg principle is a mathematical model used to calculate the allele frequencies of traits with dominant and recessive alleles. The model assumes that the population: is large has random mating is experiencing no selection has no mutation, emigration or immigration. If these assumptions are met then the allele frequencies of the population will remain stable over time. 9 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Calculating allele frequencies 10 of 37 © Boardworks Ltd 2009