* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantitative genetics
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
The Bell Curve wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Race and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
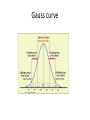
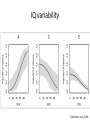
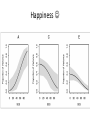
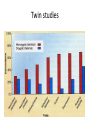
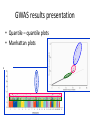
Quantitative genetics [email protected] www.imbm.sk Basics • Genotype affects phenotype • Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium • ... • Mendelian genetics is easy • ...but it works only rarely • Selection, mutation, drift... • Happiness • Always...do literature search • Environmental factors – ... • Genetic factors??? Issues • • • • • Who is happy? Is it binary or continuous? How to measure it? How to analyze genetic effects? How to find the the genetic factors? Quantitative genetics • Non-Mendelian inheritance • Polygenic traits – Many genes – Continuous variability • Categorical, treshold parameters • Multifactorial traits – Polygenic – Environmental factors Gauss curve Genetic basis for the Gauss curve Panmixia vs inbreeding • Selective vs non-selective mating • Inbreeding disturbs normal distribution – Median=mean=modus – Symmetric histogram • Decrease of heterozygosity • Reduced fitness Heritability • P = G + E + GxE • G=A+D+I • E=C+E • G - Genetic factors, E - environmental factors, GxE interactions, A - additive effects, D – dominance (alleles at one locus), E – epistasis (alles at different loci), C common and E - non-shared environment (children in one family are different) • EEE... Heritability • Variability • 1 = a2 + d2 + i2 + c2 + e2 + interactions • Heritability – h2=genetic variability/phenotypic variability – narrow 2 VA h VP • h2 = a 2 – broad • H 2 = a 2 + d2 + i 2 VG VA VD VI H VP VP 2 Heritability • Proportion of phenotypic variability attributable to genetic variability • • • • • • • Examples A statistical parameter – population measure Do not use for individuals Not a constant (place, time, population) Not specific Itself highly affected by environment Low reproducibility Heritability • Does not mean familial occurence – Genetic factors – Cultural factors – Socioeconomic variables – Chance!!! • Does not mean unmodifiable – Diabetes • Does not mean inherited! – Down syndrome, autism Heritability • Correlations – cor(P1,P2) = raa2 + rdd2 + rii2 + rcc2 • Interactions – Passive (born into), active (extroversion), reactive – evocative (attractive) – Phenylketonuria – Effect of age – Effect of socioeconomical status • Heritability and selection – Low heritability – inefficient selection IQ variability Bouchard & McGue, 2003 IQ variability Turkheimer et al, 2003. Happiness Scientific approaches • Twin studies • Adoption studies • Linkage analysis • Case-control studies – Candidate gene approach – Genome-wide association studies Twin studies • Twins – Monozygotic MZ (100% genetic relatedness) – Dizygotic DZ (50% genetic relatedness) – Concordance of traits – rMZ > rDZ – rMZ = rDZ – rMZ < 1 Twin studies • Heritability – rmz = A + C – rdz = ½A + C – A = 2 (rmz – rdz) – C = rmz – A = 2 rdz – rmz – E = 1 – rmz Twin studies Twin studies Twin studies – Environmental relatedness? • Monochorionic (2/3 MZ), dichorionic (1/3 MZ, all DZ) Twin studies Adoption studies • Genes vs environment • Biological parents vs adoptive parents • Cave: – prenatal development – selective placement – questionable representativness QTL • Quantitive trait locus/loci • Search for specific genetic factors • Locations at chromosomes, not genes • SNP or CNV marker in linkage McCarthy et al, 2008 GWAS • Cases and controls – binarization • Frequent genotypes with small effects • Large numbers – Study power – sample size • Bias – false positive results – why? • Quality control (samples and SNP calling) • Replication • Validation GWAS results presentation • Quantile – quantile plots • Manhattan plots Happiness • Twin and adoption studies – Estimates of heritability • Linkage analysis and GWAS – Search for genetic factors • Experiments – Mechanism of action – Interpretation of animal experiments – Ethics Test Psychometry • Well being questionnaire • http://www.who-5.org/ • Valid? Precise? Specific? Sensitive? • Reproducible? Statistics • • • • Tests Correlation Regression Confidence intervals