* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Catalyst
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
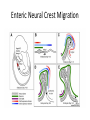
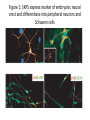
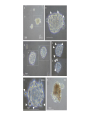
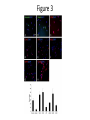
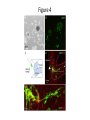
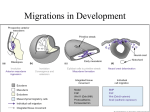
Regenerative Therapy for Hirschsprung’s Disease Harry Flaster, MD Summary • Transplantation of native or induced pluripotent stem cells has exciting potential to treat Hirschsprung’s disease • Among the many possible “cell-based” approaches to the treatment of Hirschsprung’s is the use of skin-derived precursors • This approach has its limitations • Therefore, treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease will remain operative • But, this is an exciting area of research, and HD is a great disease to study Hirschsprung’s Disease • Most common neural crest cell pathology in humans affecting 1:5000 newborns • Result of incomplete colonization of bowel with enteric neural crest cells, resulting in peristalsis, causing chronic constipation • Treatment for HD is a “pull through” procedure, where by aganglionic portions of bowel are resected and then anastomosed to healthy bowel while preserving sphincter function. Neural Crest Cells • Biologic Rebels: “they break all the rules” Enteric Nervous System • ENS is derived from neural crest cells originating in the vagal neural crest of the developing embryo • Neural crest cells delaminate from the vagal neural crest, then congregate in the caudal brachial arches, then enter the anterior foregut during the 4th week of gestation • The cells then proliferate rapidly, forming a migratory “wave” that reaches the distal hindgut by week 7.5, but it is not until week 10 that the cells coalesce into what will eventually become the myenteric plexus • Then, a few days later, there is a second centripetal wave inward, forming the submucosal plexus. Enteric Neural Crest Migration Other Neural Crest Associated Defects • Mutation in cKit migration defects • Waadenburg’s Pax3 mutation • Di George Syndrome: 22q11 deletion: disrupts neural crest migration into pharyngeal arches Abstract • Skin-derived precursor cells (SKPs) are somatic cells located in the bulge of hair follicles SKPs • Have similar properties to neural crest cells Figure 1: SKPS express marker of embryonic neural crest and differentiate into peripheral neurons and Schwann cells Materials and Methods • Foreskin tissue was collected from 5 patients, aged 2 months to 12 years old, who had undergone circumcision • Used mice with the Ret knockout mutation • Prepared both human and mice tissue were prepared in a similar fashion in order to isolate the SKPs and then grow them in culture • Both the mice and human SKPs were labeled with GFP using recombinant adenovirus in culture • The Ret knockout embyronic guts were excised and five GFP-labeled mouse and human SKP spheres were mixed with basement membrane extract than transplanted to the hindgut Ex vivo gut explants • The mouse guts were then cultured for an additional three days, then fixed, stained, and photographed • The experiments were repeated three times Results • Successfully isolated SKPs and grew SKP spheres in culture SKPs express pluripotent transcription factors • “Stemness” genes, transcription factors none to be capable of inducing pluripotency in fibroblasts, were expressed in SKPs, including Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (Oct-4 missing) • SKPs also express neural crest cell makers, but, surprisingly, not Ret Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Problems with this specific study • The SKPs express neuronal markers and look like neurons. Do they work like neurons? • “Cell migration occurs over distances between 0.60 mm and 1.03 mm and the average migration distance is 0.78 mm away from the site of transplantation.” • Even in HD limited to the sigmoid colon, both the population of transplanted enteric nervous system pluripotent cells and the distances required for them to travel would be vast • However, there is the potential for a more limited transplantation to the anastomotic region after a pullthrough Challenges to this field of research • Migration distances • Potential for neoplasm (germ cell tumor) • Will the transplanted cells restore functionality? • Are the transplanted cells sufficient? What other factors must be manipulated? To solve multi-factorial problems, it takes a multi-factorial approach Works Cited Works Cited Works Cited Works Cited Works Cited Thank You Ped Surg at SCH