* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benzodiazepines
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
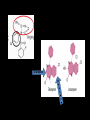
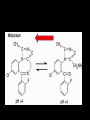
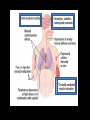
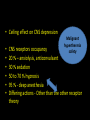
Benzodiazepines Dr. S. Parthasarathy MD., DA., DNB, MD (Acu), Dip. Diab. DCA, Dip. Software statisticsPhD ( physiology), IDRA Class of five • • • • anxiolysis, Pure anesthetic ?? sedation, anticonvulsant actions, spinal cord-mediated skeletal muscle relaxation, • anterograde (acquisition or encoding of new information) amnesia When we compare The answer is Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Sedation more Amnesia more Anesthetic Anxiolysis Safety – less More Tolerance – yes less Addiction potential – yes No Hepatic microsome no Yes Antagonist – No Flumazenil Withdrawal effects No Withdrawal effects Yes Structure • Benzene + diazepine • Benzene ring (5 carbon atoms) fused to a seven-member diazepine ring (2 • nitrogen atoms, 5 carbon atoms); • side groups are responsible for the property variations between drugs of this class Diazepine • Benzodiazepines enhance fast inhibitory neurotransmission via modulating the activity of GABA A receptors in postsynaptic membranes • Increased chloride ( hyperpolarization ) • Increased sodium is depolarization • Inhibition of neurons – same as thio but why diazepam is safe ?? • The benzodiazepines do not activate the GABA A receptors by themselves; rather, benzodiazepines modulate the response to GABA by enhancing the affinity of the receptor for GABA • It needs the neurotransmitter GABA – • They are GABA facilitators than THIO ( GABA mimetics) • Hence the safety That’s the safety factor !! Other mechanisms • benzodiazepines may be working by nonGABA mechanisms such as inhibition of adenosine reuptake • inhibition of neuronal Ca2+ currents. • (Anti convulsant predominant) • agonist activity at the glycine receptor, an important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord GABA A receptors Pictures taken from net for closed academic purpose only Supplied as • Diazepam and lorazepam are “classic” benzodiazepines that are lipid soluble and difficult to solubilize for injection. • Diazepam injection is supplied as a 0.5% solution in 40% propylene glycol and 10% ethanol. • Lorazepam is supplied as a 0.4% solution in 80% propylene glycol, 18% polyethylene glycol, and 2% benzyl alcohol. Induction doses Dose Onset durat Excita tion Pain • Elderly, debilitated , liver disease – 25 % less • Repeat doses , opioid addition- 25 % less • Alcohol !! • Sedation on induction – midazolam • 1 -2 mg IV bolus , 5 minutes , titrate with 0.75 to 1 mg bolus to get the desired effect Routes • Oral , IM and IV routes are available • The intravenous solution can be mixed with fruit juice or flavored syrup-• But IM diazepam ?? • IM midaz and ketamine are the two induction agents • Nasal, sublingual, intrathecal – Yes for midazolam Rectal • 0.4 mg / kg midazolam • 0.75 mg/ kg of diazepam • Rarely sublingual and skin patches have been used • Febrile fits in chubby child !! Intrathecal Benzodiazepines Midazolam • GABA 2 receptors in dorsal horn • Also delta receptors • 1 -2 mg – motor block , early post op analgesia • ? Prolongation of anaesthesia • 12 mg / day – chronic pain • Can be combined with opioids and clonidine • Early - neuro toxicity - ? Possibly addition of 10 % HCl in preparation – now proved as nil In CNS • • • • • Decreased CMRO2. No change in ICP No iso electric EEG No neuro protective effect But better anticonvulsant • Amnesia and sedation -- √ 1.Premedicant2. Anesthetic adjuvant – 3.Anesthetic – 4.Post op and ICU sedation – 5.Status epilepticus – 6. Tetanus -- • Ceiling effect on CNS depression • • • • • • Malignant hyperthermia safety CNS receptors occupancy 20 % – anxiolysis, anticonvulsant 30 % sedation 50 to 70 % hypnosis 95 % - deep anesthesia Differing actions - Other than the other receptor theory Debatable • benzodiazepines can reduce anxiety at doses that are not highly sedating. • Of note, the same effects may not occur in surgical patients. • Many patients scheduled for surgery do not have high levels of self-rated anxiety, • effect of midazolam is more likely to produce dizziness or sleepiness Clinical tips • Tolerance – yes • Anticonvulsant in status but tolerance – chronic seizure prophylaxis ??? • Emergence delirium; prophylaxis and treatment • Withdrawal of abuse drugs • Cardiac cath, reduce hallucinations after ketamine • Midazolam (0.5 to 1 mg IV) may be an effective treatment for the paradoxical vocal cord motion that may manifest postoperatively. Other effects • Benzodiazepines produce a mild reduction in muscle tone, which may be advantageous • Dislocations Effect on • Mechanical ventilation limbic system more than • Endoscopies cortex • Internuncial neurons in spinal cord • No effect in NMJ MAOi – OK Other effects • No effect on blood pressure • No effect on myocardial contractility • dose-dependent decrease in hypoxic ventilatory drive, also CO2 drive • Sub hypnotic doses given alone rarely cause apnea. • Make unconscious – then apnea is comparable with thiopentone • No nausea Metabolism • Midaz – hydroxy midaz – can accumulate in infusion , but high clearance for shorter duration of action of midazolam • Diazepam is principally metabolized by hepatic microsomal enzymes using an oxidative pathway of N-demethylation. • The two principal metabolites of diazepam are des methyl diazepam and oxazepam, with a lesser amount metabolized to temazepam. • That’s why - the drowsiness • It is absorbed on the plastic and cannot be removed by dialysis. All three drugs are extensively protein bound– but midaz All are lipid soluble to act in the brain Lorazepam • Higher affinity for receptors • • • • But less lipid soluble than others Cross slowly – slow onset Glucuronic acid and excreted Ideal drug for patients with liver disease and alcohol withdrawal symptoms • • • • • Side effects Fatigue Drowsiness Decreased motor coordination Impairment of cognitive function Anterograde amnesia (accentuated by concomitant ingestion of alcohol) • Paradoxical agitations ( beware of periop agitationhypoxia, inadequate reversal, full bladder etc,, ) • Suicidality • Worsen depression Drug interactions • Synergistic effects with other CNS depressants • Decreased anesthetic requirements • Potentiation of ventilatory depressant effects of opioids • Reduced analgesic effects of opioids • Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis • Dependence Diazepam Midazolam Preparation Lipid soluble Water soluble Pain on injection Yes Ring closure – no pain Dose 4-5 mg 1 mg ( potency) Metabolites Yes – hence infusion no Not very active – inf. Yes Routes Oral . IV rectal + IM, intrathecal, buccal nasal Protein bound More A little less Duration More with slurred Recovery Less with clear head Resp depression Less Slightly more Amnesia, anticonvulsant, anesthesia, sedation CVS stability – same Summary • • • • • • Structure Drugs Preparation Effects and uses Advantages Side effects