* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SoftMatter
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
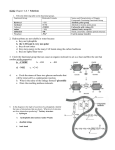
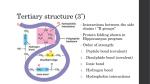
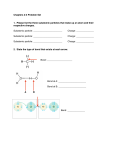
Soft Matter Soft matter is held together by the two weakest types of bonding, the hydrogen bond and the van der Waals bond. It does not exhibit the crystalline order that is characteristic of most hard matter. Nevertheless, some order remains in soft matter. It is driven by the organization of hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecular groups. That can lead to self-assembly over a wide range of sizes, all the way from nano-structures to human beings. Pierre-Gilles de Gennes received the 1991 Physics Nobel Prize for bringing order into soft matter, such as polymers and liquid crystals. Micelles Surfactant: Hydrophilic Head + Hydrophobic Tail Phospholipid = Amphiphilic Molecule Micelle: Inverse Micelle: Heads outside, Water outside Heads inside, Water inside Used for drug delivery Nano-beaker for synthesis of nanocrystals Bilayer Structures , Vesicle Part of a Cell Wall Drug Delivery via Liposomes Supramolecular Assemblies Polymers Monomer: A Oligomer: A-A-A-A Homopolymer: A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A- … Heteropolymer = Copolymer: A-B-B-A-B-A-B-A-B-A-A-B-A-B- … Block Copolymer: A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A—B-B-B-B The volume ratio of the A- and B- blocks, together with the strength of the interaction between A and B determines how they assemble themselves (see Slides 10,11). A Hydrophilic-Hydrophobic Block Copolymer PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) PS (polystyrene) Negative charge on the Neutral hydrocarbons oxygen makes it hydrophilic. make it hydrophobic. Identify Polymers by their Molecular Orbitals using X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy * Orbital EFermi Photon C 1s Core Level Phases of a Diblock Copolymer Hydrophilic + Hydrophobic Data Interaction Strength Theory Volume Fraction Volume Fraction Volume Fraction Triblock Copolymers: Even more Options Biopolymers: DNA Biopolymers: Proteins The Peptide Bond between Amino Acids in a Protein N Two amino acids react. N forms the bridge. See the * orbital of this double bond in X-ray absorption O N covalent + ionic Detect the peptide bond orbital with X-ray absorption spectroscopy at the N 1s edge Need a glycine dimer to establish the peptide bond. A. Hitchcock et al. Photon Energy [eV] The Peptide Bond and Protein Structures The peptide bond orbital spreads across O=C=N, which produces a planar arrangement. Hydrophobic interaction α-Helix β-Sheet Secondary structure Tertiary structure Protein Folding Hierarchy Schematic of Hemoglobin Protein Infrared Spectroscopy Vibrations reveal the secondary and tertiary structure. oxygen 0.008 +400 mV Amide vibrational modes: b -sheet 0.006 random turn S • Amide I, C=O stretch secondary structure a-helix: 1649-1658 cm-1 b-sheet: 1620-1635 cm-1 a-helix • Amide II, N-H bend tertiary structure HD exchange: 15501450 cm-1 0.004 0.002 0.000 1600 1620 1640 1660 1680 -1 Wavenumber / cm J. Lipkowski 1700