* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tertiary structure (3*)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
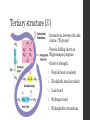
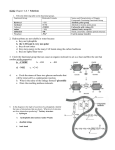
Tertiary structure (3˚)
2)
1)
3)
4)
•
Interactions between the side
chains / “R groups”
•
Protein folding shown in
Hippocampus program
•
Order of strength:
1.
Peptide bond (covalent)
2.
Disulphide bond (covalent)
3.
Ionic bond
4.
Hydrogen bond
5.
Hydrophobic interactions
Quaternary structure (4˚)
•
2 or more polypeptide chains joined together
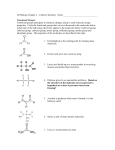
Polarity & Hydrophilic/phobicity
•
“Hydro” in hydrophobic/hydrophilic refers to Water, which is
POLAR
•
Therefore polar R groups of amino acids will be hydrophilic as
it will be able to hydrogen bond with water molecules.
•
Non-polar R groups of amino acids will be hydrophobic because
the hydrophobic R groups would repel the polar water
molecules
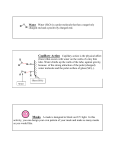
Free or Anti-social in Water (polar)?
Anti-social: Don’t want
anything to do with
water molecules
Freely
interacting with
water molecules
Bond to each other
{
Free or Anti-social in Oil (non-polar)?
Freely
interacting with
oil molecules
Anti-social: Don’t want
anything to do with oil
molecules
Bond to each other
{
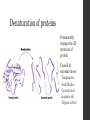
Denaturation of proteins
•
Permanently
changes the 3D
structure of
protein
•
Caused by
external stress:
-Temperature
-Acid/Alkaline
-Concentrated
inorganic salt
-Organic solvent
Functions of Proteins
•
Support structure: e.g. cytoskeleton, cartilage, bone
•
Enzymes: catalyze reactions
•
Monitors: changing shape according to signals
•
Intercellular communication