* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes part 1
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Co-operation (evolution) wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of ageing wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
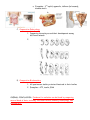
Name NOTES Date Period XBIO: Evolution Notes I. History A. Disproving Spontaneous Generation/Abiogenesis 1. Redi________ - meat in 2 jars, one covered other uncovered 2. Spallanzani___ - broth in 2 flasks, one sealed other unsealed 3. Pasteur____ - flask with curved neck B. Conclusion: Biogenesis – life can only arise from life II. Early Theory of Evolution A. Lamarck 1. Theory of Use and Disuse 2. If an organism uses an organ it will become stronger 3. If an organism does not use an organ it will disappear 4. These acquired characteristics can be passed onto offspring DO YOU THINK HE WAS CORRECT???? B. Giraffe Example C. ??? If I work out a lot and become huge – will my offspring be born with big muscles ??? Why or why not? D. ??? If I color my hair red – will my offspring be born with red hair ??? Why or why not? E. Conclusion: Acquired characteristics are NOT coded in DNA, therefore they CANNOT be passed onto offspring F. Conclusion: Lamarck theory was INCORRECT III. Darwin – Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection A. Trip – HMS Beagle to the Galapagos Islands B. Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection i. Living things overproduce ii. There is (genetic) variation among offspring iii. There is a struggle to survive iv. Natural selection is always taking place C. Natural Selection – the process by which the most fit organisms reproduce D. Survival of the Fittest – Reproductive success i. Individuals whose characteristics are well suited to their environment survive AND REPRODUCE ii. Individuals whose characteristics are not well suited to their environment with die AND leave fewer or no offspring iii. Therefore – those individuals “more fit” survive to produce offspring with their “more fit” characteristics iv. Example – peppered moths (see slide) E. Adaptations – variations in populations that have an advantage over others in the same population (refer back to peppered moths) IV. Evidence for Evolution A. Fossils 1. In sedimentary rock 2. Imprints in soft sediment that hardens 3. Petrification – replacement of bones by minerals 4. Amber – think Jurassic Park B. Comparative Anatomy 1. HOMOLOGOUS Structures – structures are similar but with different functions (share a common ancestor) a. Example – arm of a person, wing of a bird b. 2. ANALOGOUS Structures – structures are different but have similar functions (evolved independently) a. Example – wing of a bee, wing of a bird 3. VESTIGIAL ORGANS/Structures – structures that no longer have a useful function a. Examples – 3rd eyelid, appendix, tailbone (in humans), wisdom teeth b. c. C. Comparative Embryology 1. Comparing the embryos and their development among different animals 2. D. Comaprative Biochemistry 1. All species use similar proteins/chemicals in their bodies 2. Examples – ATP, insulin, DNA OVERALL CONCLUSION: Evidence for evolution can be found by comparing several kinds of data, including: the fossil record, anatomy, embryology, and biochemistry.