* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COMPLEMENT activation - Akademik Ciamik 2010
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Complement component 4 wikipedia , lookup
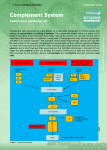
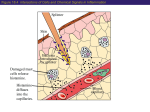
Anna Tjandrawati Clinical Pathology Department Medical Faculty Padjadjaran University Hasan sadikin General Hosptital Bandung HOST DEFENSES IN INNATE IMMUNITY Cells Antigen presenting cells Basophils Eosinophils Mast cells Phagocytes Humoral factors Complement proteins Lactoferrin Lysozyme Pepsin Stomach acidity Anatomical barriers Cilia Mucus Skin Resident flora Mainly nonpathogenic bacteria COMPLEMENT Definition : a system comprised of a groups of plasma and cell membrane proteins that play an important role in host defense process. Components: More than 30 proteins Synthesized in the liver, macrophages and other cells Functions : Lysis of cells, bacteria, and viruses Opsonization, which promotes phagocytosis of particulate antigens. Regulate inflammatory and immune responses Regulate the biologic activity of cells. CLASSICAL PATHWAY ALTERNATIVE PATHWAY MANNAN BINDING LECTIN PATHWAY COMPLEMENT activation As a cascade Numerous protein of the complement system are sequentially activated. Activation typically refers to the conversion zymogen to an enzymatic form The enzymatic form cleave other complement protein into two fragments COMPLEMENT activation Some fragments bind to receptors, while others bind to microbial surfaces One complement fragment associates with intact protein to form cytocidal complexes that insert into the membranes of cells ( bacteria) resulting in bacteria destruction C3 convertase classical pathway C3 convertase alternative pathway C5 convertase classical pathway C5 convertase alternative pathway Protein Abbreviation Regulatory Function C1 inhibitor C1 INH Binds to C1, thereby preventing it from initiating complement activation. Properdin Properdin Stabilizes the alternative pathway C3 convertase C4 binding protein C4bp Accelerates the dissociation of both C3 convertases. Decay accelerating factor DAF Accelerates the dissociation of both C3 convertases. Factor I (plus a cofactor) Factor I Cleaves and inactivates C3b and C4b. Anaphylatoxin inhibitor AI Proteolytically cleaves the anaphylatoxins. Membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis. MIRL of CD 59 Inhibits MAC formation Homogenous restriction factor HRF Inhibits MAC formation. S-protein (also known as Vitronectin) S-protein Inhibits MAC formation. Receptor Complement Ligand Cell Type for Receptor Receptor.-Ligand Interaction Function CR1 C3b and iC3b Phagocytes Erythrocyte •Opsonin mediated recognition of antigen •Clearance of circulating immune complex CR2 iC3b B lymphocytes Mode of Epstein Barr virus infection CR3 iC3b Phagocytes Cellular adhesion Opsonin mediated recognition of antigen CR4 iC3b Phagocytes Opsonin mediated recognition of antigen C3a/ C4a-R C3a and C4a Mast cell and basophils Degranulation that leads to release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators C5a-R C5a Mast cell and Basophils Endothelial cells Phagocytes Degranulation that leads to release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators Increase vascular permeability Chemotaxis. Biological activity of complement Inflammatory response : C3a, C4a, C 5a - Anaphylatoxins - Chemokines/Chemotaxis Phagocytosis: C3b - Opsonin Elimination of immune complex: C3b - Opsonin and receptors Osmotic lysis bacteria:C5b6789 - MAC(Membrane Attack Complex) Deficiency Disorder C1 INH Hereditary angioneurotic edema (HANE) C2 and C4 Immune complex disorders often present in individual with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) C3 Pyogenic infections with encapsulated bacteria C5,6,7,8,9 Recurent infections with Neisseria spp. GPI Linkages (DAF, Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria CD59) Measurement of Overall Complement Activity CH50 and AH50 Measurement of Complement Components Radial Immunodiffusion (RID) Nephelometry rate nephelometry: an assay in which the rate of immune complex formation is measured