* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
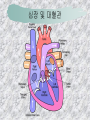
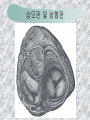
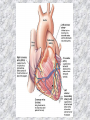
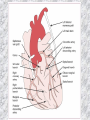
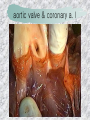
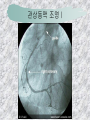
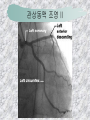
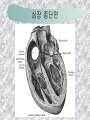
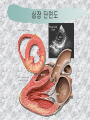
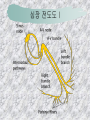
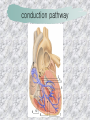
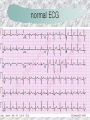
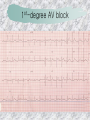
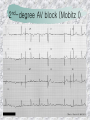
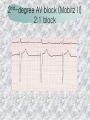
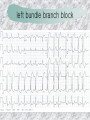
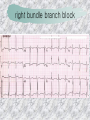
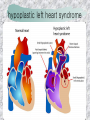
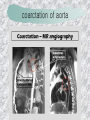
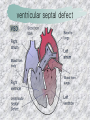
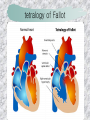
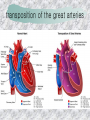
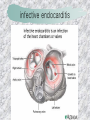
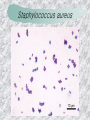
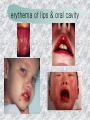
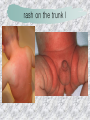
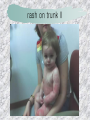
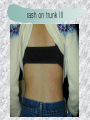
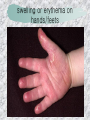
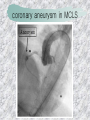
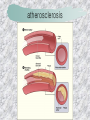
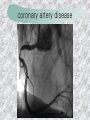
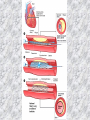
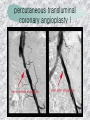
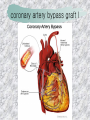
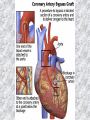
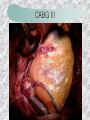
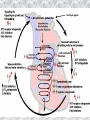
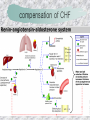
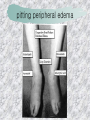
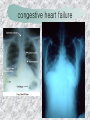
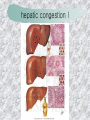
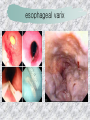
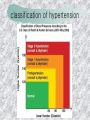
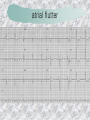
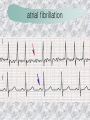
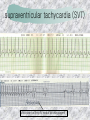
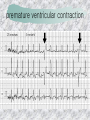
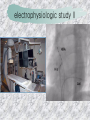
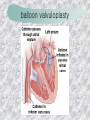
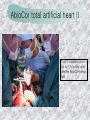
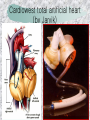
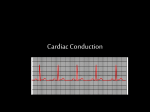
기본 의학 용어 의공학교실 박성근 table 1. 의학용어의 특징 2. 인체의 기본구조 3. 병리학적 검사분야 4. 방사선과학적 검사분야 5. 임상병리 검사분야 6. 핵의학 검사분야 7. 약물요법 분야 8. 소화기계질환 분야 9. 심혈관계질환 분야 10. 호흡기계질환 분야 11. 근골격계질환 분야 12. 신경 및 정신계질환 분 야 13. 비뇨기계 및 남성생식기 계질환 분야 14. 내분비계 및 여성생식기 계질환 분야 15. 피부과, 안과 및 이비인 후과질환 분야 16. 병원의 진료 편제 심장 및 대혈관 승모판 및 삼첨판 대동맥판막 및 폐동맥판막 aortic valve & coronary a. I aortic valve & coronary a. II 관상동맥 조영 I 관상동맥 조영 II 해부학적 용어 vena cava: 대정맥 superior vena cava (SVC): 상대정맥 inferior vena cava (IVC): 하대정맥 right atrium (pl. atria, RA): 우심방 tricuspid valve: 삼첨판 pulmonic (pulmonary) valve: 폐동맥 판(막) pulmonary artery (PA): 폐동맥 pulmonary (pulmonic) vein: 폐정맥 left atrium (pl. atria, LA): 좌심방 mitral valve: 승모판 left ventricle (LV): 좌 심실 aortic valve: 대동맥 판 (막) aorta: 대동맥 valve (leaflet): 판막(엽) coronary a.: 관상동맥 심장 종단면 심장 단면도 심장 전도도 I 심장 전도도 II sinoatrial node (SA node, sinus node) located in RA autonomous innervation atrioventricular node (AV node) sympathetic n. (T1-4) vagus n. (CN X) located in posteroinf. region of interatrial septum 심장 전도도 III AV bundle (bundle of His) located in ventricular septum Purkinje fiber divides into two bundle branches located in the inner ventricular walls specialized myocardial fibers that conduct an electrical stimulus conduction pathway conduction & ECG 심혈관계 질환 분야 heart wall structure (inter)atrial septum: 심방중격 (inter)ventricular septum: 심실중격 endocardium: 심내막 myocardium: 심근(층) epicardium: 심외막 pericardium: 심막, 심 낭 conduction system S-A (sinoatrial) node: 동결절 A-V (atrioventricular) node: 방실결절 atrioventricular bundle: 방실속 purkinje fiber: 퍼킨지 섬유 심혈관계 질환 분야 others diastole: 확장기, 이완 기 systole: 수축기 blood pressure (BP): 혈압 심혈관계 질환 분야 증상 용어 angina pectoris: 협심 (증) arrhythmia, dysrhythmia: 부정맥 heart block: 심(장)블 록 bradycardia: 서맥 tachycardia: 빈박, 빈 맥 cardiac arrest: 심박동 정지 (heart, cardiac) murmur: (심)잡음 cyanosis: 청색증 precordial pain: 흉통, 전흉부 통증 regurgitation: 역류, 부 전 stenosis: 협착 atresia: 폐쇄(증) 심혈관계 질환 분야 판막명 + regurgitation, insufficiency, stenosis, atresia = 판막질환 병 명 e.g., aortic regurgitation: 대 동맥판막 부전증 aortic stenosis: 대동맥 판막 협착증 tricuspid regurgitation: 삼첨판막 부전증 tricuspid stenosis: 삼첨 판막 협착증 pulmonary atresia: 폐동 맥판막 폐쇄증 tricuspid atresia: 삼첨판 막 폐쇄증 ECG analysis duration ECG elements analysis P wave atrial depolarization QRS complex the depolarization of the right and left ventricles. PR interval duration of conduction from SA node to ventricles 120 to 200 ms long. ST segment MI indicator 80 to 120 ms long T wave the repolarization (or recovery) of the ventricles normal ECG heart block I types SA nodal blocks AV nodal blocks infra-Hisian block SA nodal blocks absent P wave on an ECG subtypes c.f., SA node suppression: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation AV nodal blocks subtypes Wenckebach (Mobitz I) Mobitz II exit block 1st degree AV block (PR prolongation > 0.20 s) 2nd degree AV block (one or more (but not all) of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles) 3rd degree AV block heart block II 2nd degree AV block Wenckebach (Mobitz I): prolongation of PR int. on consecutive beats followed by a blocked P wave -> AV node dis. Mobitz II: intermittently nonconducted P waves not preceded by PR prolongation and not followed by PR shortening -> HisPurkinje sys. dis. 3rd degree AV block (complete heart block): impulse of the SA node does not propagate to the ventricles -> ventricular escape rhythm, i.e., P waves & QRS complexes are totally independent infra-Hisian block subtypes Mobitz II left bundle branch bl. right bundle branch bl. 1st-degree AV block 2nd-degree AV block (Mobitz I) 2nd-degree AV block (Mobitz II) 2:1 block 3rd-degree AV block heart block III LBBB supraventricular rhythm QRS dur. => 120 ms QS or rS in V1 monophasic R in I & V6 RBBB supraventricular rhythm QRS dur. => 100 ms (incomplete block) QRS dur. => 120 ms (complete block) terminal R in V1 slurred S in I & V6 left bundle branch block right bundle branch block 심혈관계 질환 분야 질환명 congenital heart disease (CHD): 선천 성 심장질환 VSD (ventricular septal defect): 심실중 격결손증 ASD (atrial septal defect): 심방중격결손 증 PDA (patent ductus arteriosus): 동맥관개 존(증) tetralogy of Fallot (TOF): 팔로사징[증] TGA (transposition of the great arteries): 완 전대혈관전위증 SBE (subacute bacterial endocarditis): 아급성 (세균성) 심내막 염 myocarditis: 심근염 pericarditis: 심낭염, 심막염 congenital heart disease hypoplasia hypoplastic left heart syndrome hypoplastic right heart syndrome septal defects obstruction defects pulmonary valve stenosis aortic valve stenosis coarctation of aorta atrial septal defect (ASD): patent foramen ovale ventricular septal defect (VSD) cyanotic defects tetralogy of Fallot transposition of the great arteries persistent ductus arteriosus hypoplastic left heart syndrome coarctation of aorta ventricular septal defect tetralogy of Fallot transposition of the great arteries infective endocarditis acute fulminant illness over days to weeks (less than about 6 weeks) greater virulence mainly Staphylococcus aureus subacute progresses slowly over weeks and months low propensity to hematogenously seed extracardiac sites mainly streptococci infective endocarditis Staphylococcus aureus streptococci 심혈관계 질환 분야 rheumatic (valvular) heart disease: 류마티 스[성] 심질환 acute rheumatic fever: 급성 류마트열 Kawasaki disease (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome): 가와사끼 질환 (피부점막림프절 증후군) congestive heart failure: 울혈성 심부전 coronary artery disease: 관상동맥질환 ischemic heart disease: 허혈성 심질 환 myocardial infarction: 심근경색 cardiomyopathy: 심근 (병)증 rheumatic heart disease I acute rheumatic fever complication of a respiratory infections caused by the group A streptococcus (GAS) M-protein -> Ab that cross-react with autoantigens on interstitial connective tissue (endocardium, synovium) clinical Diagnosis: 2 major or 1 major + 2 minor revised Jones’ major criteria pancarditis migratory polyarthritis subcutaneous nodule erythema marginatum sydenham chorea (involuntary, purposeless movement) rheumatic heart disease II minor criteria fever arthralgia raised ESR or CRP leukocytosis heart block ECG evidence of Strep. infection: elevated antistreptolysin O titre or DNAse previous episode of rheumatic fever or inactive heart disease treatment aspirin high dose (100 mg/kg/day) steroids for heart involvement -> prevent sequelae such as MS monthly injections of long-acting penicillin for 5 yrs (if carditis -> for 40 yrs) continual use of low dose antibiotics to prevent recurrence mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome Kawasaki disease autoimmune disease clinical diagnosis: 5 days of fever + 4 of 5 diagnostic criteria erythema of the lips or oral cavity or cracking of the lips rash on the trunk swelling or erythema of the hands or feet red eyes (conjunctival injection) swollen lymph node in the neck of at least 15 mm cardiac complication is of major concern: coronary aneurysm treatment hospitalization i.v. immunoglobulin aspirin steroid erythema of lips & oral cavity rash on the trunk I rash on trunk II rash on trunk III swelling or erythema on hands/feets red eye Kawasaki disease coronary aneurysm in MCLS ischemic heart disease disease characterized by reduced blood supply to the heart muscle major cause: coronary artery disease risk factors: age, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, hypertension, male, family history signs and symptoms medical treatment angina pectoris acute chest pain myocardial infarction heart failure antianginal drugs: nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers surgical treatment PTCA CABG atherosclerosis coronary artery disease percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty I coronary artery bypass graft I CABG III heart failure I cardiac output is insufficient for the body’s needs classifications left HF vs right HF backward vs forward low output vs high output LHF symptoms & signs (pulm. congestion) dyspnea on exertion orthopnea paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea rales (pulm. edema) dullness of the lung fields to percussion (pleural effusion) cyanosis (hypoxemia) heart failure II compromise of LV forward function (enlarged heart) gallop rhythm (valvular heart disease): AS or MR symptoms & signs (systemic capillary congestion) apex beat (increased bl. flow) dizziness confusion cool extremities at rest RHF murmur pitting peripheral edema or anasarca nocturia ascites hepatomegaly -> jaundice, coagulopathy NYHA Functional Classification NYHA Class Symptoms I No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity, e.g. shortness of breath when walking, climbing stairs etc. II Mild symptoms (mild shortness of breath and/or angina) an d slight limitation during ordinary activity. III Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms, even during le ss-than-ordinary activity, e.g. walking short distances (20100 m). Comfortable only at rest. IV Severe limitations. Experiences symptoms even while at rest . Mostly bedbound patients. causes of CHF in US IHD: 62 % smoking: 16 % hypertension: 10 % obesity: 8 % diabetes: 3 % VHD: 2 % in Italy IHD: 40 % dilated CMP: 32 % VHD: 12 % hypertension: 11 % others: 5 % rarer causes viral myocarditis amyloidosis HIV cardiomyopathy systemic lupus erythematosus abuse of drugs such as alcohol pharmaceutical drugs such as chemotherapeutic agents arrhythmias compensation of CHF pitting peripheral edema congestive heart failure hepatic congestion I hepatic congestion II esophageal varix chronic management of CHF goals to prevent the acute decompensated HF to counteract the cardiac remodeling to minimize symptom medical Tx. oral loop diuretics beta-blockers ACE inhibitors angiotensin receptor blockers vasodilators aldosterone receptor antagonists in severe cardiomyopathy behavioral modification reduced salt & fliud exercise when tolerated heart transplantation 심혈관계 질환 분야 hypertension: 고혈압 hypotension: 저혈압 paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT): 발 작성 상심실성 빈맥 ventricular tachycardia: 심실성 빈 맥 검사, 치료 및 수술 용 어 (pericardio)centesis: 심낭천자 cardiac massage: 심 장 마사지 artificial pacemaker: 인공심박조율기 cardioversion, defibrillation: 전기적 제세동 cardioverter, defibrillator: 제세동기 24 hours Holter monitoring (ambulatory ECG): 24 시간 심전도 hypertension Systolic pressure Diastolic pressure Classification mmHg kPa (kN/m2) mmHg kPa (kN/m2) Normal 90–119 12–15.9 60–79 8.0–10.5 Prehypertension 120–139 16.0–18.5 80–89 10.7–11.9 Stage 1 140–159 18.7–21.2 90–99 12.0–13.2 Stage 2 ≥160 ≥21.3 ≥100 ≥13.3 Isolated systolic hypertension ≥140 ≥18.7 <90 <12.0 classification of hypertension etiology of hypertension essential HT primary HT no medical cause 90 – 95 % secondary HT renovascular HT renal artery stenosis -> HT HT secondary to other renal disorders CRF renal segmental hypoplasia HT secondary to endocrine disorders pheochromocytoma -> adrenaline secretion Cushing’s syndrome etc. other secondary HT hormonal contraceptive pregnancy drugs: alcohol, NSAIDs, steoids nephron million nephrons / kidney complication of HT hypotension etiology hypovolemia: hemorrhage, insufficient fluid intake, diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics decreased cardiac output: congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, bradycardia, arrhythmia, beta blockers excessive vasodilation: neurologic, sepsis, acidosis, medications symptoms dizziness fainting and/or seizures treatment volume resuscitation blood pressure support: norepinephrine adequate tissue perfusion: SvO2 > 70% with additional pressors address the underlying problem: antibiotic, stent, CABG, steroid arrhythmia I 빈맥 vs. 서맥 tachycardia: > 100 beats/min bradycardia: < 60 beats/min common classification atrial premature atrial contractions (PACs) wandering atrial pacemaker multifocal atrial tachycardia atrial flutter (230 – 380 beats/min) atrial fibrillation (Afib) junctional arrhythmias supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) AV nodal reentrant tachycardia junctional rhythm junctional tachycardia arrhythmia II atrioventricular AV reentrant tachycardia: WolffParkinson-White syndrome, LownGanong-Levine syndrome heart blocks premature ventricular contractions (PVC) accelerated idioventricular rhythm monomorphic ventricular tachycardia 1st degree heart block 2nd degree heart block: ventricular polymorphic ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation Mobitz I or Wenckebach Mobitz II 3rd degree heart block (complete heart block) atrial flutter atrial fibrillation supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) ultra short acting AV nodal blocking agent premature ventricular contraction ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach) ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) 심혈관계 질환 분야 EKG, ECG (electrocardiogram, electrocardiography): 심전도 echocardiography: 심 에코검사, 심장초음파 검사 electrophysiologic study (EPS, EP study): 전기생리검사 cardiac catheterization: 심도 자법, 심도자검사 interventional catheterization: 중재 적 심도자검사 balloon coronary angioplasty: 풍선 관상 동맥성형술 balloon valvuloplasty: 풍선 판막성형술 balloon angioplasty: 풍선 혈관성형술 heart-lung machine: 인공심폐 [장치], 심폐 기 echocardiography echocardiography II electrophysiologic study I electrophysiologic study II balloon valvuloplasty heart-lung machine I John H. Gibbon Jr., the original designer and de veloper of the heart-lun g machine, performed th e first successful openheart surgery on a patie nt with congenital heart disease on 6 May 1953. 심혈관계 질환 분야 heart transplantation: 심장 이식 artificial heart: 인공심 장 cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR): 심폐소생술 coronary artery bypass graft (CABG): 관상동맥 우회로 이식 (술) coronary care unit (CCU): 관동맥질환 집 중치료병동 intensive care unit (ICU): 중환자실 postsurgical intensive care unit (PICU): 수술 후 중환자실 heart transplantation I first human heart transplant by Surgeon Christiaan Barnard on the 3rd December 1967. 18 days later the patient died fr om double pneumonia heart transplantation II A comparison of the old and new hearts of Dylan Stork, the smallest heart transplant recipient in th e world. Dylan weighed 5.5 pounds (2.5 kilogra ms) at the time of the op eration. (Reproduced by permission of Photo Res earchers, Inc.) korean total artificial heart (KORTAH) AbioCor total artificial heart I AbioCor total artificial heart II Tom Christerson surviv ed for 17 months after another AbioCor transp lant Cardiowest total artificial heart (by Jarvik) 심혈관계 질환 분야 동맥, 모세혈관, 정맥 에 관한 용어 artery: 동맥 arteriole: 세동맥, 소동 맥 capillary: 모세혈관 venule: 세정맥, 소정맥 vein: 정맥 infarction: 경색형성, 경색[증] ischemia: 국소빈혈, 허혈 arteritis: 동맥염 phlebitis: 정맥염 thrombophlebitis: 혈 전[성] 정맥염 aneurysm: 동맥류 arteriosclerosis: 동맥 경화[증] atherosclerosis: 아테 롬성 [동맥]경화증 embolism: 색전증 심혈관계 질환 분야 thrombosis: 혈전증 varicose veins, varicosity: 정맥류 embolectomy: 색전절 제[술] thrombectomy; 혈전절 제술