* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrhythmias 3
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
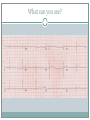
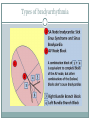
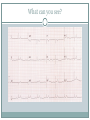
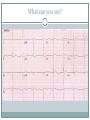
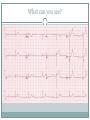
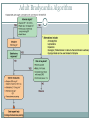
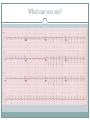
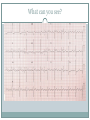
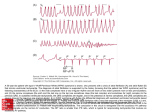
Arrhythmias YASMINE DARWAZEH FY1 – GENERAL SURGERY Objectives Define bradyarrhythmia and tachyarrythmia Know the most common brady- & tachyarrythmias Recognise them on an ECG. Know the main signs and symptoms, aetiology and treatments of each. What can you see? Types of bradyarrhythmia Sinus Bradycardia HR < 60bpm Causes Physiological (normal in athletic people) Iatrogenic (Beta blockers, Ca channel blockers, digoxin, anticholinergics) Hypothyroidism Metabolic e.g. hyperkalemia Hypoxia Hypothermia Acute MI/ischemia Treatment Remove cause (ie drugs) Treat cause (ie hypothyroidism) What can you see? 1st degree AV node block PR interval >0.2secs (more than 5 small squares) Delayed conduction through/near the AVN Usually asymptomatic Narrow QRS complex indicates block within AVN Wide QRS complex indicates His-Purkinje block. Causes MI Myocarditis/endocarditis SLE Treatment Usually benign Can progress to other forms of AV block If symptomatic, consider pacemaker What can you see? Mobitz type 1 (Wenkebach) PR interval progressively lengthens until a P wave is not followed by a QRS complex. Continues as a cycle. Due to a conduction defect within the AVN Causes: • Inferior MI • Drugs • Myocarditis Treatment • None required (unless reversible cause) What can you see? Mobitz type 2 Intermittent non-conducting P waves. May occur in regular pattern e.g. every 3rd p wave is not followed by a QRS complex (3:1 block) Causes Anterior MI Inflammatory (rheumatic fever, myocarditis) Autoimmune (SLE, systemic sclerosis) Hyperkalaemia Infiltration (sarcoid, haemochromatosis, amyloid) Treatment Internal pacing eventually as likely to progress to 3rd degree heart block What can you see? Complete AV block Complete dissociation between atrial & ventricular depolarisations All impulses from atria blocked by the AVN Very symptomatic & very syncopal. Causes Inferior MI Drugs (ca channel blockers, beta blockers, digoxin) Progression of Mobitz 1 & II Congenital (if mother has SLE) Lev's disease: idiopathic fibrosis & calcification of conducting system Treatment Internal pacing Adult Bradycardia Algorithm What can you see? Sinus tachycardia HR > 100bpm Causes: Intra-cardiac causes Ishcaemic heart disease Valvular heart disease Heart failure Cardiomyopathy Congenital heart disease Treatment Treat the cause. Extra-cardiac causes •Drugs •Alcohol •Stimulants e.g. caffeine •Stress •Hyperthyroidism •Infection/Sepsis Broad and Narrow Complex tachycardias Broad Complex Tachyarrhythmias Ventricular Tachycardia Torsades de Pointes Ventricular Fibrillation Narrow Complex Tachyarrhythmias (Supraventricular Tachycardias) Sinus Tachycardia Atrial Tachycardia Reentrant Tachycardias (AVNRT and AVRT) Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter What can you see? Atrial Flutter SVT, regular Saw-tooth flutter waves. Flutter waves rate = 300 bpm Ventricular rate = 150 bpm or 100 bpm, due to AVN block ratio of 2:1 or 3:1 Ectopic atrial beat causes a re-entrant circuit within the atria. Causes As for AF Hyperkalaemia Digoxin toxicity. Treatment As for AF (discussed later) Can be differentiated from Fast AF with vagal manouvres/adenosine. What can you see? Ventricular tachycardia Broad complex tachycardia Causes • Electrolyte derangement (hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia, hypocalcaemia) • Myocardial ischaemia/infarct • Cardiomyopathy • Congenital (HOCM, long QT) Treatment • Amiodarone • ICDs What can you see? Atrial Fibrillation Atria chaotically fibrillate. Fibrillation rate between 350 & 600bpm. Variable impulse conduction through the AVN Irregularly irregular rhythm Most common arrhythmia. 10% of population >80 years old. Significant morbidity due to thromboembolic disease Unmanaged = 5% yearly stroke risk. Atrial Fibrillation Types Paroxysmal (acute onset, spontaneous termination within 1 week) Persistent (>7 days, can be cardioverted) Permanent (> 1 year not terminated by cardioversion) Causes Cardio (HTN, valvular disease, CAD, myositis) Pulmonary (PE, pneumonia, COPD, lung Ca) Metabolic (hyperthyroidism) Infection Drugs (alcohol, illicit drugs) AF Investigations Bedside – ECG/24 hour tape Bloods – FBC, U&Es, LFTs, TFTs, coag screen Imaging – CXR, echo Management (Rate vs Rhythm) Rate – Beta blockers Digoxin Rhythm Cardioversion Sotalol Amiodarone (HF) AF - CHA2DS2-VASc score Thromboprophylaxis C – cardiac failure (1) H – HTN (1) A - >75 (2, 1 if 65-74) D – diabetes (1) S- stroke/TIA (2) Va – vascular disease Sc – female (1) 0 = Low Risk 1 = Moderate risk 2 or more = high risk Summary Define bradyarrhythmia and tachyarrythmia Know the most common brady- & tachyarrythmias Recognise them on an ECG. Know the main signs and symptoms, aetiology and treatments of each. Any Questions