* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preoperative Evaluation and Risk Assessment in the Cardiac
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
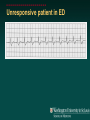
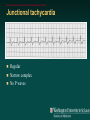
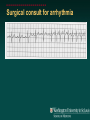
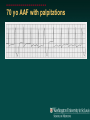
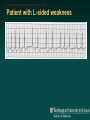
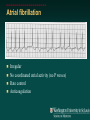
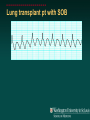
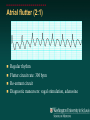
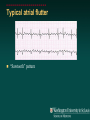
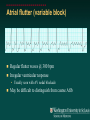
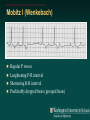
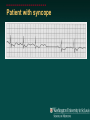
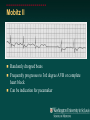
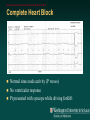
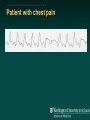
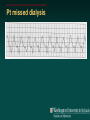
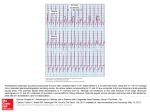
Telemetry / Arrythmias Dan Crouch Kristi Kuhn Kate Lindley Ben Voss Unresponsive patient in ED Junctional tachycardia Regular Narrow complex No P waves Surgical consult for arrhythmia Paroxysmal SVT (PAT) Benign rhythm If sustained: • Vagal maneuvers • Adenosine • DCCV 70 yo AAF with palpitations Premature ventricular complexes Abnormal but usually benign • Concerns: very frequent, history of ischemia Ask about symptoms (palpitations, “skipping a beat”) • Beta-blockers for symptomatic patients Called to see sleeping patient NSVT ICM or NICM • Usually not an indication for ICD Ask about symptoms Use more beta-blockers Patient with L-sided weakness Atrial fibrillation Irregular No coordinated atrial activity (no P waves) Rate control Anticoagulation Lung transplant pt with SOB Atrial flutter (2:1) Regular rhythm Flutter circuit rate: 300 bpm Re-entrant circuit Diagnostic maneuvers: vagal stimulation, adenosine Typical atrial flutter “Sawtooth” pattern Atrial flutter (variable block) Regular flutter waves @ 300 bpm Irregular ventricular response • Usually seen with AV nodal blockade May be difficult to distinguish from coarse Afib Nursing student asks for help Mobitz I (Wenkebach) Regular P waves Lengthening P-R interval Shortening R-R interval Predictably dropped beats (grouped beats) Patient with syncope Mobitz II Randomly dropped beats Frequently progresses to 3rd degree AVB or complete heart block Can be indication for pacemaker 27 yo WM with syncope at work Complete Heart Block Normal sinus node activity (P waves) No ventricular response Pt presented with syncope while driving forklift Patient with chest pain Ventricular tachycardia Wide complex tachycardias • VT until proven otherwise for patients with ischemia • Brugada criteria: only AV dissociation useful on tele – GET AN EKG!! • Non-malignant rhythm with aberrancy also possible Pt missed dialysis Hyperkalemia QRS widening Peaked T waves Treatment: • Calcium first • Insulin/glucose, albuterol, glucagon, NaHCO3, IVF/Lasix • Kayexalate last 18 yo WF postpartum Torsades de pointes Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Life-threatening with degeneration to VF Usually precipitated by PVC in setting of long QT Often associated with QT-prolonging drugs Check for electrolyte disturbances (especially Mg) Regardless of the telemetry…