* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atrial Flutter
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
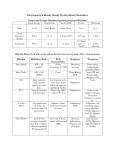
Atrial Flutter Definition: Well-organised but overly rapid contractions of the atrium of the heart Usually 250-300 contractions per minute Rapid vibration or pulsation Difference between fibrillation and flutter is that flutter is organised Causes: Occurs most often in individuals with CV disease: HT, CAD, cardiomyioathy, etc) May occur spontaneously in people with otherwise normal hearts Not a stable rhythm atrial fibriliation Clinical features: Sometimes asymptomatic Onset characterised by sensations of regular palpitations Usually well tolerated (high heart rate for most people is a normal response to exercise), however those with underlying conditions may experience: SOB, chest pains, lightheadedness, nausea and in some patients, nervousness and feelings of impending doom Complications: Rate related ventricular decomposition and heart failure Clot formation: poor contraction of the atria leads to stasis of blood in the atria clot formation Sudden cardiac death (due to AF) Treatment (same as atrial fibriliation): Anticoagulation Rate control versus rhythm control using drugs Rate control Cardioversion: electrical DC shock Ablation