* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular Physiology part-2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
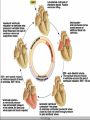
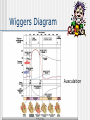
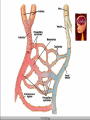
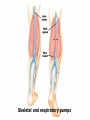
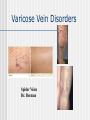
Following our way through the Cardiac Cycle: Step by step… Atria and ventricles at rest Atrial Systole: 20% of ventricular filling Early ventricular contraction Obtain first heart sound: AV valves close “lub” EDV Isolvolumic ventricular contraction Our second heart sound: semilunar valves close “dup” ESV Isovolumetric relaxation Ventricular Ejection Ventricular relaxation We’re back to atrial and ventricular relaxation Wiggers Diagram Ausculation Can we measure how much blood your heart pumps? CO=SV X Heart Rate What determines our stroke volume? Stroke volume influenced by Length of muscle fiber contractility Frank-Starling Law (length of muscle fiber) Contractility influence by Norepinephrine Drugs: in the news today! digitalis Chapter 15 Blood Flow Blood Pressure and Control of blood pressure Picture 15-3 Then, how then does blood from your extremities get back to heart from these low pressure veins? Skeletal and respiratory pumps Varicose Vein Disorders Spider Veins Dr. Berman Measurements of blood pressure NORMAL BP RANGES •Systolic between 90 and 135 mmHg Diastolic between 50 and 90 mmHg 1. Pulse pressure Systolic pressure-Diastolic pressure measures strength of pressure wave 2. MEAN ARTERIAL PRESSURE MAP=1/3 Pulse Pressure + Diastolic pressure MAP provides a single value that does not show a all the changes of arterial pressure. Blood Pressure Day 1 Day 2 120/90 160/70 Now by calculating the mean arterial pressure, on which day is blood flow greatest to the tissues? Local Controllers of Blood pressure Myogenic autoregulation Paracrines and smooth muscle Chemical affects on our blood vessels Norepinepherine Serotonin NO Histamine Epinephrine Vasocontriction Vasodilation Migraines: inappropriate vasodilation Sumatriptan Serotonin agonist Affect of some paracrines Active hyperemia Reactive hyperemia Coordination of blood pressure Control Baroreceptors stretch Action potentials to CNS ANS