* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Heart Muscle Mechanics: Part 3
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
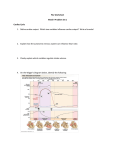
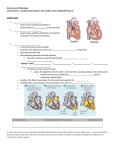
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Heart Muscle Mechanics: Part 3 152615 >>> 0:00:00.2 SLIDE 1 of 2 Table V-2-1 Reflex Changes For Specific Maneuvers Condition Aff. Activity Para. Sym. BP increase BP decrease BP HR Carotid Occlusion Carotid massage Cut Afferents Lying to stand Orthostatic hypotension Fluid loss toward normal Volume Load Weightlessness toward normal 152620 >>> 0:11:56 SLIDE 2 of 2 CARDIAC CYCLE Normal Cardiac Cycle A volume-pressure diagram of the left ventricle during one cardiac cycle of a normal heart is shown above. Which point on the diagram corresponds to the second heart sound? (A) Point A (B) Point B (C) Point C (D) Point D (E) Point E (F) Point F (G) Point G (H) Point H >Explanations Explanations: The correct answer is E. The various points on the volume-pressure diagram correspond to specific events of the cardiac cycle as follows: Choice A: Marks the beginning of systole. The mitral valve closes and S1 can be heard. The end diastolic pressure (5 mmHg) and end diastolic volume (125 mL) can be determined on the Y-axis and X-axis from this point. Choice B: This is the period of isovolumic contraction. Left ventricular pressure increases rapidly, but left ventricular volume remains constant. All heart valves are closed. Choice C: The aortic valve opens, which marks the beginning of the period of ejection. The pressure at this point is equal to the diastolic blood pressure, which is about 80 mmHg on the diagram. Choice D: This is the period of ejection. The pressure at the apex of the curve is the peak systolic pressure of the left ventricle. Choice E: Marks the beginning of diastole. The aortic valve closes and S2 can be heard. The end systolic volume (50 mL) can be read from the X-axis at this point. Choice F: The is the period of isovolumic relaxation. Left ventricular pressure is falling rapidly, but left ventricular volume remains constant. All heart valves are closed. Choice G: The mitral valve opens and the period of filling begins. Choice H: This is the period of filling. Return to Question