* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Treadmill Stress Testing for the Primary Care Physician
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
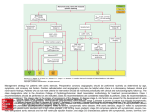
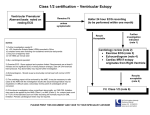
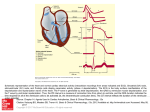
Majelle L. Gagtan Definition Indications/Contraindications Running the Exercise Test Protocols Non-invasive procedure providing information about changes in rate, rhythm, conductionn and ventricular repolarization as the heart responds to exertion Exposes the heart to the stress of exercise thus unmasking s/sx of heart disease, and the ECG may produce characteristic abnormalities Patients with s/sx suggestive of CAD Patients with significant risk factors for CAD To evaluate exercise tolerance in patients with unexplained fatigue and shortness of breath To evaluate BP response to exercise in patients with borderline hypertension To look for exercise-induced serious irregular heart beats Recent acute MI Severe aortic stenosis Unstable angina Active myocarditis Ventricular tachycardia Thrombophlebitis or Dissecting aortic intracardiac thrombi Recent pulmonary embolus Acute infection aneurysm Acute CHF Uncontrolled severe Complex ventricular ectopy hypertension Moderate aortic stenosis Severe subaortic stenosis Supraventricular dysrhythmias Ventricular aneurysm Cardiomyopathy Uncontrolled metabolic disease Recurrent infectious disease Complicated pregnancy HR and BP are recorded at rest 12L ECG is recorded Start at a relatively slow “warm up” speed then its speed and inclination are increased every 3 mins. according to a preprogrammed protocol BP is recorded every minute Stopped when the patient achieves target HR, or if he develops chest discomfort, dyspnea, dizziness etc., or if the ECG showed significant changes It may also be stopped if BP rises or falls beyond acceptable limits Maximum HR = 220 – age of patient BRUCE Protocol multi stage maximal treadmill protocol with 3-min periods to allow achievement of steady state before workload is increased Modified BRUCE Protocol 2 3-min warm-up stages at 1.7mph and 0% grade and 1.7mph and 5% grade For older individuals or those with exercise capacity is limited by cardiac disease Naughton and Weber protocols • 1 2-min stages with 1 MET increments between stages • More suitable for patients with limited exercise tolerance Asymptomatic Cardiac Ishemia Pilot Trial (ACIP) and modified ACIP protocols • For pxs with established CAD • Results in linear increase in HR and VO2 • Modified ACIP – similar aerobic demand; well suited for short or elderly who can’t keep up with a walking speed of 3mph ST Depression → or ↓ ≥ 1mm at 60msec ↑ ≥ 1.5mm at 80msec ST Elevation ≥ 1mm at 60msec No change ST depression doesn’t fulfill no.2 T wave inversion w/o ST segment changes ST elevatoin in a Q wave lead Dyspnea, fatigue, chest pain Systolic blood pressure drop Technical difficulties ECG--ST changes, arrhythmias Signs of poor perfusion (cyanosis/pallor) Px’s desire to stop Achievement of maximal exercise