* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Chemistry of Life
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
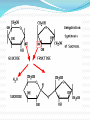
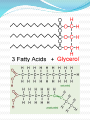
Chapter 2 Part 2 II. Chemistry of Life A. Organic Chemistry 1. a. b. c. d. Biosynthesis Living things putting together substances Scientists have been trying to create life They’ve made simple proteins Is this morally acceptable? http://www.cnn.com/2010/HEALTH/05/21/venter.qa/index.html 2. Organic compounds a. Must have carbon in it b. Carbon covalently bonds c. Carbon can form straight and branched chains, rings, single, double, or triple bonds d. Provides A LOT of possibilities e. Functions 1) Structural – help with cell walls/membrane 2) Enzymatic – enzymes 3) Storage – store energy f. 4 main groups (Table 2B-1 pg 58) 1) Carbohydrates 2) Lipids 3) Proteins 4) Nucleic acids 3. Carbs and Lipids 1) Carbohydrates a) Have C, H, O b) Store energy c) Monosaccharides i. Simple sugars ii. Basic unit of carbs iii. Glucose – sugar from plants iv. Ribose and fructose d) Disaccharides i. Monosaccharides joined together ii. Dehydration synthesis – water is given off i) Sucrose – table sugar ii) Lactose – milk sugar iii. Hydrolysis – disaccharides broken down by water to make monosaccharide e) Polysaccharides i. Large molecule of monosaccharides ii. Enzymes build or break them down iii. Starch – energy storage for plants iv. Glycogen – energy storage for animals v. Cellulose i) In plant walls ii) Humans can’t digest iii) Why is it important? vi. Chitin i) Hard coverings ii) Insects, lobsters, shrimp, clams, fingernails 2) Lipids a) Intro i. Help with structure ii. Store extra energy iii. Can store 2x more energy than muscle iv. Semi-soluble b) Fatty Acids i. Most abundant ii. Has hydrophilic/phobic parts i) Hydrophilic – likes water ii) Hydrophobic – doesn’t like water iii. Triglycerides i) Fats ii) Stores energy iii) Has 3 fatty acids iv) Saturated – single bonds, unhealthy, solid at room temp v) Unsaturated – double bonds, liquid iv. Phospholipids i) Two fatty acid molecules ii) Makes cell membranes 4. Proteins and Nucleic Acids a. Proteins 1) Make a person unique 2) Needed for every function 3) C, H, O, N, plus others 4) Amino acids a) Building blocks b) Organisms use 20 different a.a. c) We can make 12 d) Order of a.a. = certain protein e) Held together by peptide bonds f) Forms a polypeptide chain g) A.a. fold into a 3D shape h) If shape is broken = might not function b. Nucleic Acids 1) Make DNA and RNA 2) Blue print for organisms B. Enzymes Catalyst – lowers activation energy for reaction to occur 2. Enzyme – biological catalyst a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required 1. d. “Energy coupons” – get services or products at a reduced cost e. Disruption of homeostasis prevents enzymes from functioning (fever, hypo/hyperthermia) f. Function best in a small range of conditions g. Temp and pH changes break H-bonds h. Shape determines function i. Lock and Key model Substrates bind to an enzyme at certain places called active sites. The enzyme brings substrates together and weakens their bonds. The catalyzed reaction forms a product that is released from the enzyme.