* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Review II Answer Key
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
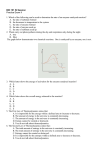
Semester Review Practice Exam 51. What is the purpose of oxygen in aerobic respiration? a. Oxygen accepts electrons at the end of an electron transport chain. b. Oxygen is necessary to carry away the waste CO2. c. Oxygen is used in the formation of sugar molecules. d. The oxygen molecule becomes part of the ATP molecule. e. Oxygen donates H+ used in the formation of NADH. 52. All of the following processes produce ATP EXCEPT: a. Glycolysis b. The Krebs cycle c. Lactate fermentation d. Oxidative phosphorylation e. Photophosphorylation Questions 53 – 54 The graph below shows the relationship between CO2 uptake by leaves and the concentrations of O2 (percent of atmosphere in growth chambers) and CO2 (ppm in growth chambers). 53. The relative CO2 uptake is a measure of a. Photosynthetic rate b. Light intensity c. Water stress d. Leaf size e. Leaf temperature 54. According to the graph, the relative CO2 uptake is best under which of the following conditions? a. 100 ppm CO2, 20% O2 b. 100 ppm CO2, 40% O2 c. 100 ppm CO2, 80% O2 d. 200 ppm CO2, 20% O2 e. 200 ppm CO2, 80% O2 Questions 55 – 59 refer to the diagram below. The three boxes represent the three major biosynthetic pathways in aerobic respiration. Arrows represent net reactants or products. 55. Arrow 2 is a. O2 b. ATP c. H2O d. FADH2 e. Pyruvate 56. Arrows 4, 8, and 12 could all be a. NADH b. ATP c. H2O d. FAD+ e. FADH2 57. Arrows 3 and 7 could both be a. NADH b. ATP c. H2O d. FAD+ e. FADH2 58. Arrow 9 could be a. O2 b. ATP c. H2O d. FAD+ e. FADH2 59. Pathway B is a. Oxidative phosphorylation b. Photophosphorylation c. The Calvin-Benson cycle d. The Krebs cycle e. Glycolysis 60. Which of the following sequences correctly indicates the potential ATP yield of the indicated molecules from greatest ATP yield to least ATP yield? a. Pyruvate, ethanol, glucose, acetyl CoA b. Glucose, pyruvate, acetyl CoA, NADH c. Glucose, pyruvate, NADH, acetyl CoA d. Glucose, FADH2, acetyl CoA, pyruvate e. Glucose, FADH2, NADH, pyruvate Questions 61 – 62 refer to the graph below that shows the amount of CO2 that is produced by plant cells at various levels of atmosphere oxygen. 61. At levels of atmospheric O2 below 1%, the amount of CO2 released is relatively high. This is probably because a. The Krebs cycle is very active b. O2 is being converted to H2O c. Alcoholic fermentation is occurring d. There are insufficient amounts of coenzyme A e. Photosynthesis cannot function at night 62. As levels of O2 increase beyond 5%, the amounts of CO2 released increase. This is probably a direct result of a. An increase in glycolytic activity b. A greater availability of appropriate enzymes c. An increase in Krebs cycle activity d. An increase in atmospheric temperature e. A decrease in the pH of the cytoplasm 63. After strenuous exercise, a muscle cell would contain increased amounts of all of the following EXCEPT: a. ADP b. CO2 c. Lactate d. Glucose e. Pi 64. Chemiosmotic theory describes how ATP is generated from ADP. All of the following statements conform to the principles of the theory EXCEPT: a. H+ accumulate in the area between the membrane of the cristae and the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. b. A pH gradient is created across the cristae membranes. c. A voltage gradient is created across the cristae membranes. d. A proton gradient is created across the cristae membranes. e. Electrons flowing through the ATP synthase channel protein provide the energy to phosphorylate ADP to ATP. 65. All of the following statements about respiration are true EXCEPT: a. Some of the products in the breakdown of proteins enter the Krebs cycle. b. Some of the products in the breakdown of lipids enter the Krebs cycle. c. Anaerobic respiration is probably a more primitive energy-yielding pathway than is aerobic respiration. d. The purpose of oxygen in aerobic respiration is to donate the electrons that transform NAD+ + H+ to NADH. e. Oxygen is required to break down lactate. 66. All of the following processes release CO2 EXCEPT: a. The Krebs cycle b. Alcoholic fermentation c. Oxidative phosphorylation d. The conversion of pyruvate to ethanol e. The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA 67. If a cell has 46 chromosomes at the beginning of mitosis, then at anaphase there would be a total of a. 23 chromatids b. 23 chromosomes c. 46 chromosomes d. 46 chromatids e. 92 chromosomes 68. If a cell has 46 chromosomes at the beginning of meiosis, then at anaphase I there would be a total of a. 23 chromatids b. 23 chromosomes c. 46 chromosomes d. 46 chromatids e. 92 chromosomes 69. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT: a. Spindle fibers are composed largely of microtubules. b. Centrioles consist of nine triplets of microtubules arranged in a circle. c. All eukaryotic cells have centrioles. d. All eukaryotic cells have a spindle apparatus. e. Many of the microtubules in a spindle apparatus attach to kinetochores to chromosomes. Questions 70 – 73 refer to a mitotically dividing cell and to the lettered answer choices below. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. B. C. D. E. Anaphase Telophase Metaphase Prophase Interphase 70. Cytokinesis begins. B 71. Chromosomes begin migrating to opposite poles. A 72. MTOCs migrate to opposite poles. D 73. Chromosomes replicate. E Questions 74 – 75 refer to the following figures. Figure (A) represents a normal diploid cell with 2n = 8. 74. A zygote. A 75. A gamete. C 76. Crossing over occurs during a. Prophase of mitosis b. Prophase I of meiosis c. Prophase II of meiosis d. Prophase I and II of meiosis e. Prophase of mitosis and prophase I of meiosis 77. In typical cell divisions by mitosis and meiosis, all of the following contribute to genetic variation EXCEPT: a. Anaphase of mitosis b. Anaphase of meiosis I c. Fertilization d. Crossing over e. Random union of egg and sperm Questions 78 – 82 refer to the cell illustrations below. The normal diploid number for the cells illustrated is four chromosomes. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. 78. Anaphase II C 79. Telophase II D 85. Some people are able to roll their tongues into a Ushape. The ability to do this is inherited as an autosomal dominant allele. What is the probability that children descendent from parents both heterozygous for this trait will be able to form a U-shape with their tongues? a. 0 b. ¼ c. ½ d. ¾ e. 1 86. In fruit flies, dumpy wings are shorter and broader than normal wings. The allele for normal wings (D) is dominant to the allele for dumpy wings (d). Two normal-winged flies were mated and produced 300 normal-winged and 100 dumpy-winged flies. The parents were probably a. DD and DD b. DD and Dd c. Dd and Dd d. Dd and dd e. dd and dd 87. Which of the following is true of the gametes produced by an individual with genotype Dd? a. ½ D and ½ D b. ½ D and ½ d c. ½ Dd and ½ dD d. All Dd e. All d 88. Suppose that in sheep, a dominant allele (B) produces black hair and a recessive allele (b) produces white hair. If you saw a black sheep, you would be able to identify a. Its phenotype for hair color b. Its genotype for hair color c. The genotypes for only one of its parents d. The genotypes for both of its parents e. The phenotypes for both of its parents For questions 89-91, use the following key. Each answer in the key may be used once, more than once, or not at all. 80. Metaphase II B 81. Metaphase of mitosis A 82. Metaphase I E 83. If you roll a pair of dice, what is the probability that they will both turn up a three? a. 1/2 b. 1/4 c. 1/8 d. 1/16 e. 1/36 84. Which of the following best expresses the concept of the word “allele”? a. Genes for wrinkled and yellow b. Genes for wrinkled and round c. The expression of a gene d. Phenotypes e. Mutations A. B. C. D. E. 0 1/16 3/16 9/16 1 In fruit flies, the gene for curved wings (c) and the gene for spineless bristles (s) are on different chromosomes. The respective wild-type alleles for each of these genes produce normal wings and normal bristles. 89. From the cross CCSS x ccss, what is the probability of having an offspring that is CcSs? E 90. From the cross CcSs x CcSs, what is the probability of having an offspring that is ccss? B 91. From the cross CcSs x CcSs, what is the probability of having an offspring that is normal for both traits? D Questions 92 – 93 In snapdragons, the allele of tall plants (T) is dominant to the allele for dwarf plants (t), and the allele for red flowers (R) is codominant with the allele for white flowers (R’). The heterozygous condition for flower color is pink (RR’). 92. If a dwarf red snapdragon is crossed with a white snapdragon homozygous for tall, what are the probable genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation? a. All TtRR’ (tall and pink) b. All TtRR (tall and red) c. All TtR’R’ (tall and white) d. All ttRR (dwarf and red) e. All ttR’R’ (dwarf and white) 93. If ttRR’ is crossed with TtRR, what would be the probable frequency for offspring that are dwarf and white? a. 0 b. ¼ c. ½ d. ¾ e. 1 94. The inheritance of skin color in humans is an example of which of the following? a. Pleiotropy b. Codominance c. Epistasis d. Polygenic inheritance e. Gene linkage 95. Red-headed people frequently have freckles. This is best explained by which of the following? a. The genes for these two traits are linked on the same chromosome. b. The genes for these two traits are sex-linked. c. Nondisjunction occurs frequently with chromosomes bearing these traits. d. Alleles for these two traits are codominant. e. Both parents have red hair and freckles. 96. Let A and a represent two alleles for one gene and B and b represent two alleles for a second gene. If for a particular individual, A and B were on one chromosome and a and b were on a second chromosome, then all of the following are true EXCEPT: a. The two genes are linked. b. The two chromosomes are homologous. c. All gametes would be either AB or ab. d. The genotype of this individual is AaBb. e. An offspring of this individual could have the genotype AABB. 97. Four genes, J, K, L, and M, reside on the same chromosome. Given that the crossover frequency between K and J is 3, between K and L is 8, between J and M is 12, and between L and M is 7, what is the order of the genes on the chromosome? a. J K L M b. J K M L c. K J L M d. K J M L e. K L J M Questions 98 – 100 refer to the following pedigree. Circles indicate females, and squares indicate males. A horizontal line connecting a male and female indicate that these two individuals produced offspring. Offspring are indicated by a descending vertical line that branches to the offspring. A filled circle or filled square indicates that the individual has a particular trait, in this case, red-green color blindness. Color blindness is inherited as a sex-linked, recessive allele. For questions 98 – 100, use the following key. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. XN XN B. XN Xn C. Xn Xn D. XN Y E. Xn Y 98. Identify the genotype for individual 10. E 99. Identify the genotype for individual 5. B 100. Identify the genotype for individual 14. B