* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cannabinoid receptors
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Medical cannabis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
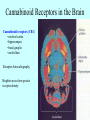
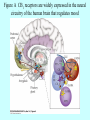
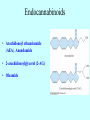
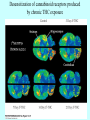
Marijuana Marijuana is a mixture of dried and crumbled leaves, small stems, and flowering tops from cannabis sativa. It can be consumed orally, as in cookies or brownies, but is usually smoked in rolled cigarettes known as “joints,” various kinds of pipes, or in hollowed-out cigars called “blunts.” The psychoactive compound Δ9tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), accounts for the use of cannabis as a drug. Marijuana potency (in terms of THC content) varies widely, depending on the genetic strain of the plant and growing conditions. Potency can be increased by preventing pollination and seed production by the female plants. This marijuana is called sinsemilla (“without seeds”). #1 most widely used illegal drug in US It is classified as a mild hallucinogen History of Marijuana • • • • Cannabis probably originated in China. Medical and religious use can be traced to ancient China, India, and the Middle East, spreading to the Arab world. Napoleon’s soldiers brought it to France from Egypt. It became popular with French writers and artists. Hemp was grown in colonial America, but marijuana smoking probably came to the U.S. with Mexican and Caribbean immigrants in the early 1900s. In 1937, the Marijuana Tax Act instituted a national registration and taxation system aimed at discouraging all use of cannabis. It was overturned in 1969, but cannabis is still tightly controlled History of Marijuana In the 1930s, the US Bureau of Narcotics launched a public relations campaign to portray marijuana as a social menace that could destroy the youth of America. The propaganda included magazine articles and antimarijuana films such as Reefer Madness. History of Marijuana Marijuana remains a controversial subject in our society—castigated by many as a gateway to the socalled hard drugs, but praised by others as an unappreciated medical marvel. Marijuana is produced from flowering hemp (Cannabis sativa). Hemp has been a major source of fiber in many cultures for rope, cloth, and paper. Hemp seeds have been used for oil and bird food. Hemp also contains 70 unique compounds known as cannabinoids, plus more than 400 other identified compounds. Hashish Hashish is a cannabis derivative that can be smoked or eaten. It can refer to a relatively pure resin preparation with very high cannabinoid content, or a solvent extract of leaves or resin. Hash oil is an alcoholic extract. A drop is placed on a tobacco or marijuana cigarette. 9-tetrahydro-cannabinol (THC) THC was identified as the major active ingredient in 1964. Burning marijuana causes the THC to vaporize and enter the smoker’s lungs in small particles. Effective dose and latency to onset of effects are influenced by the amount and potency of the plant used, and patterns of smoking (e.g., breathhold duration). THC is easily absorbed by the lungs, and blood plasma levels rise quickly. Concentrations begin to decline as a result of metabolism in the liver and accumulation in the body’s fat stores. In oral use, poor absorption results in low and variable plasma levels, probably due to degradation in the stomach and first-pass metabolism. 9-tetrahydro-cannabinol (THC) Blood THC levels decline rapidly after smoking marijuana, but complete elimination from the body is much slower because of persistence in fat tissues. The gradual movement of THC metabolites back out of fat stores means that urine screening tests can detect them more than 2 weeks after a single marijuana use. Cannabinoid Receptors • A cannabinoid receptor in the CNS was identified in 1988. • Receptors occur in many brain areas. • Cannabinoid receptors are metabotropic – – – work via G proteins to inhibit cAMP formation inhibit voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels open K+ channels. • CB1 receptors – – – • CNS Located on axon terminals Inhibiting many neurotransmitters CB2 receptors – – – – immune system Bone adipose (fat) cells GI tract. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Brain Cannabinoid receptors (CB1) •cerebral cortex •hippocampus •basal ganglia •cerebellum Receptor Autoradiography Brighter areas show greater receptor density Figure A CB1 receptors are widely expressed in the neural circuitry of the human brain that regulates mood Cnr1 Expression Endocannabinoids • Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), Anandamide • 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) • Oleamide Endocannabinoids Retrograde messengers: carry information in the opposite direction Phytocannabinoids Cannabigerol-type CBG Cannabielsoin-type CBE Cannabichromene-type CBC isoTetrahydrocannabinoltype iso-THC Cannabidiol-type CBD Cannabicyclol-type CBL Tetrahydrocannabinoland Cannabinol-type THC, CBN Cannabicitran-type CBT Probability of initiating marijuana use as a function of age Effects of Marijuana Negative Effects: lung damage Impaired tracking ability memory loss reduced locomotor activity hypothermia hypoalgesia adversely affect cognitive function anxiety or paranoia decreased sperm cell count altering of mood addiction like properties tolerance formation desensitization of receptors Amotivational syndrome Gateway drug? Positive Effects: reduced nausea reduced pain reduced MS spasticity reduced symptoms of GI tract disorders reduced cancer formation reduced symptoms of neurodegenerative disorders reduced symptoms of psychiatric disorders CB1 antagonists can reduce obesity fear alleviation Hippocampal CB1 receptors are responsible for memory impairment Acquisition of THC selfadministration by squirrel monkeys Time course of overall withdrawal discomfort in heavy marijuana users undergoing abstinence Desensitization of cannabinoid receptors produced by chronic THC exposure The New Medicinal Marijuana • THC • CBD Cannabis and Multiple Sclerosis Cannabidiol (CBD) •Pain •Shaking •Spasms •Spasticity •Fatigue •Sleep Quality •Mobility •Well Being Cannabis and Cancer MMP-2: enzyme that promotes spread of cancer