* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matters of Sex - Old Saybrook Public Schools
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
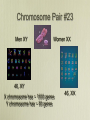
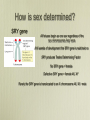
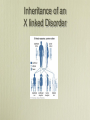
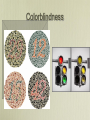
Matters of Sex Genetic Disorders Related to the Sex Chromosomes Chromosome Pair #23 Men XY Women XX 46, XY X chromosome has ~ 1500 genes Y chromosome has ~ 80 genes 46, XX Does the mom or the dad determine the sex of a child? DAD How is sex determined? SRY gene All fetuses begin as one sex regardless of the sex chromosomes they have At 6 weeks of development the SRY gene is switched on SRY produces Testes Determining Factor No SRY gene = female Defective SRY gene = female 46, XY Rarely the SRY gene is translocated to an X chromosome 46, XX male Hermaphroditism Greek God Hermes and Goddess Aphrodite • Both sex organs (ovotestes) • Female masculinity forms when mother has excess testosterone while pregnant (ovarian tumors) • Male feminine forms due to problems with testosterone production because of malfunctioning of the SRY gene X-linked Disorders • X chromosome genes important for normal functioning • Women have 2 X chromosomes • Men have 1 X chromosome • Mutation in a gene on the X then a woman has a back-up copy a man does not, disorders more common in men • Man inherits his X from his mother Inheritance of an X linked Disorder X Linked Disorders • Colorblindness • Hemophilia • Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Colorblindness Colorblindness Inheritance 6 % of men 0.4 % of women Hemophilia Normal gene on X codes for clotting factors 1 : 10,000 men 1 : 100 million women Queen Victoria passed the mutation to the royal bloodlines of Europe Inheritance of Hemophilia Muscular Dystrophy Gene for dystrophin (muscle protein) is mutated 1 : 3000 males