* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.1 Earth`s Formation
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
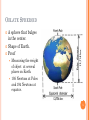
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
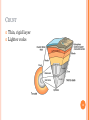
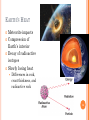
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
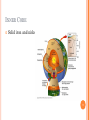
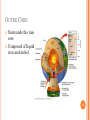
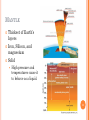
4.1 EARTH’S FORMATION 1 DAHS Mr. Sweet OBJECTIVES Explain how most scientists explain the formation of our solar system. Describe Earth’s size and shape and the arrangement of its layers. List three sources of Earth’s internal heat. Describe Earth’s magnetic field. 2 NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS Most widely accepted model for solar system formation 4.6 billion years ago Cloud of gas and dust rotating in space Shrank due to pull of gravity, spinning faster Material collected at center and became hot. Hydrogen fusion began creating our sun. 3 PLANETISMALS Frictional, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces formed solid particles of ice and rock. Eventually formed planets and moons. 4 OBLATE SPHEROID A sphere that bulges in the center. Shape of Earth. Proof Measuring the weight of object at several places on Earth. 195 Newtons at Poles and 194 Newtons at equator. 5 EARTH’S MEASUREMENTS Total surface area 510 million square km 55 continental USA’s 149 million square km is above sea level Ocean covers 361 million square km 29% dry, 71% wet 6 ORIGINAL EARTH Looked like the moon Same material all the way thru Collisions created heat Heat melted iron and nickel Denser material moved to the center and lighter materials to the surface 7 LAYERS OF EARTH Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Lithosphere Asthenosphere Crust 8 INNER CORE Solid iron and nickel 9 OUTER CORE Surrounds the inner core Composed of liquid iron and nickel 10 MANTLE Thickest of Earth’s layers Iron, Silicon, and magnesium Solid High pressure and temperatures cause it to behave as a liquid. 11 CRUST Thin, rigid layer Lighter rocks 12 OTHERS Lithosphere Crust and uppermost mantle More rigid material Asthenosphere Slushlike layer of mantle Lithosphere floats on top Cause of plate tectonics 13 EARTH’S HEAT Meteorite impacts Compression of Earth’s interior Decay of radioactive isotopes Slowly losing heat Differences in rock, crust thickness, and radioactive rock 14 TEMPERATURE AT DEPTH Above 70 feet temperature remains constant year round Below 70 feet temperature rises 1o Celcius every 40 meters 15 MAGNETIC FIELD North Pole is the positive pole South Pole is the negative pole Tilted 11O away from the poles Hypothesized that the fluid outer core creates the magnetic field Iron moves through and electric field creating another electric field 16 SECTION REVIEW 4.1 Page 74 Numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 17