* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Structure of the Earth
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
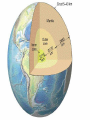
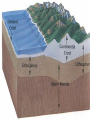
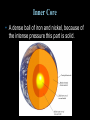
Unit 1: Structure of the Earth Standard: Compare and Contrast the layers of the earth including composition, relative temperature, and density. The Crust • Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin including the solid earth and oceans. • Composition: oxygen, silicon, aluminum, calcium, iron, sodium, potassium, and magnesium • Relative Temperature: Vary from air temperature to 870 oC • Density: 2.5 to 3.0 times denser than water The Mantle • Layer of hot rock between the crust and core. • Composition: silicon, oxygen, iron, and magnesium • Relative Temperature: 870oC to 2,200oC • Density: 3.3 to 5.5 times denser than water. The Core • Center of the Earth; under extreme pressure • Composition: iron and nickel • Relative Temperature: 2,000oC to 5,000oC • Density: 10 to 13 times denser than water Crust Mantle Lithosphere Asthenosphere Lithosphere • The rigid layer formed from the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust together. • Averages 100 km thick Asthenosphere • Upper part of the Mantle. • Molten (melted) rock layer. About 175 km thick. Outer Core • Area of molten metal that surrounds the inner core. Because the earth rotates, the outer core spins around the inner core and that causes the earth's magnetism. Inner Core • A dense ball of iron and nickel, because of the intense pressure this part is solid. `