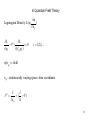* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Euler Lagrange Equation
Kaluza–Klein theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
An Exceptionally Simple Theory of Everything wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Feynman diagram wikipedia , lookup
BRST quantization wikipedia , lookup
Scale invariance wikipedia , lookup
Gauge fixing wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Light-front quantization applications wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Yang–Mills theory wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
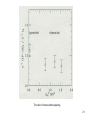
Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics By Leila Joulaeizadeh 19 Oct. 2005 1- Literature : Lattice QCD , C. Davis Hep-ph/0205181 2- Burcham and Jobes 1 Outline - Introduction - Hamilton principle - Local gauge invariance and QED - Local gauge invariance and QCD - Lattice QCD calculations - Some results - Conclusion 2 What is Quantum Chromodynamics and why LQCD? - Strong interaction between coloured quarks by exchange of coloured gluon - Gluons carry colour so they have self interaction - Self interaction of gluons , nonabelian group SU(3) - QCD is a nonlinear theory so there is no analytical solution and we should use numerical methods 3 Euler Lagrange Equation x1 I x1 f ( y, y ' )dx for minimising I I f ( y, y ' )dx 0 x0 x0 y(x 0 ) y(x1 ) 0 x1 x0 y' d y dx x1 ( f f f f d y ' y ' )dx ( y ' ( y))dx y y y y dx x 0 U sin g partial integratio n and y(x) 0 f d f 0 y dx y ' 4 For motion of a point like particle with mass m in a central potential: L 1 m( x 2 y 2 z 2 ) V(r ) 2 L V Fx x x L mx Px x L d L 0 x dt x generaliza tion t1 Action S L.dt is minimized t0 L d L 0 q i dt q i Hamilton Principle Physical systems will evolve in such a way to minimize the action 5 In Quantum Field Theory Lagrangian Density : L( , ) x L L ( )0 i ( i ) i 1,2,3,... (x ) field x : continuously varying space - time coordinate ( , ) x t 6 Examples Scalar field (spin 0 particle) 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 L ( )( ) m g ( )( ) m 2 2 2 2 m2 0 Klein - Gordon Eq. Spinor field(spin 1/2 particle) _ _ _ _ L i m i m 0 Dirac eq. 7 Local Gauge Invariance and QED Transforma tion parameter is a function of x : (x) ' exp[ iq ( x )] ( x ) , ' exp[ iq ( x )] ( x ) For a free Dirac particle of mass m : L i m After local gauge transformation : L' i exp[ iq ( x )] ( x ) (exp[ iq ( x )] ( x )) m exp[ iq ( x )] ( x ) exp[ iq ( x )] ( x ) i q m L Gauge covariant derivative : D iqA ( x ) , D exp[ iq ( x )]D , A ( x ) A ( x ) - ( x ) L i D m i m qA L free j A j q 8 We add kinetic energy term : L L free j A 1 FFμν 4 If the photon were not massless : L F A A 1 2 1 m A A L' m 2 (A )( A ) L 2 2 Example Massless vector field(spin 1) 1 L FF j A F j 4 Covariant form of Maxwell equation 9 Local Gauge Invariance and QCD q ' q exp[ ig s a ( x )Ta ] q ( x ) Ta , Tb if abcTc , q ' q exp[ ig s a ( x )Ta ] ' q ( x ) SU(3) group generators For a free Dirac particle of mass m : L i j q qk m q q j q j q q After local gauge transformation : L' L D ig s Ta Ba , Ba ( x ) Ba ( x ) - a ( x ) g s f abc b ( x )Bc ( x ) Non-Abelian nature of SU(3) L i q D q m q q q i q q m q q q g s ( q Ta q )Ba We add kinetic term : L j i q (D ) jk qk q (D ) jk jk ig s (Ta ) jk Ba q m q qj qj 1 a BBa 4 a 1,2,...,8 b c a B Ba Ba g s f abc B B Gluon self interaction term B D B D B 10 Diagrams representing propagation of free quark and gluon and their interaction 11 Lattice QCD O : operator whose expectation value we want to calculate 0O0 S d [ d ] dA O [ , , A ] e d[d ]dA e After discretisation : d 4 x n S a 4 , (x, t) (n i a, n t a) a : spacing between the points n Scalar field theory lagrangian L Lattice action : S S Ld 4 x 1 1 ( ) 2 m 2 2 2 2 2 4 (n 1 ) (n 1 ) 1 2 2 4 1 a ( m (n )) 2 1 2a 2 12 Lattice gauge theory for gluons Gluon field in continuum B b x X+1 U (x) U e Gluon field in lattice U ( g ) ( x ) ikgB G ( x ) U ( x )G ( x 1) X+1 U - (x 1) U 1 U (x) 1 ikgB g x (x) G(x) (x) g (x) (x) G (x) G G 1 G ( x ) : Gauge transformation matrix closed loop of gluon U p (x) U i (x)U j (x 1i )U i (x 1 j )U j (x) string of gluon field U ( x1 )... U ( x 2 Wilson plaquette action : Slatt 6 a 0.1(fm) TrU p requires calibratio n! 1 ) U ( x 2 ) Purely gluonic piece of continum QCD action : d4x x2 _ 1 4g 2 6 x1 x Tr (BB ) g2 13 Lattice gauge theory for gluons Feynman path integral : 0 O 0 S dU Oe S dU e U O e S After discretiza tion : 0O0 U : a set of U matrices U e S one for each link in lattice O : the value of O operator in that configurat ion Importance sampling : choose configurat ions with large contributi ons to the integral 14 Fermion doubling problem of quarks on the lattice Continuum action for a single flavor of free fermions : _ S f d x ( m ) 4 Fourier tr ansformation of L f : 1 Continuum inverse propagator: G -cont ( p ) i p m 0 Naive lattice dicretizat ion : 4 _ x 1 x 1 naive 4 Slatt, a m x x x f 2 a n 1 Fourier tr ansformation of L f : 1 lattice inverse propagator: G -latt, naive ( p) i sin p a a m p a 0 a 2 4 fermions instead of 1 !! 15 Solutions of Fermion doubling problem Wilson quarks Sfw Sfnaive r a5 2 4 ( x 1 2 x x 1 x x 1` a 2 ) r Wilson parameter Problem : Larger discretiza tion errors! a 0 Sfw Sfnaive Staggered quarks Interpretation of doublers as diffrent flavours Problem : Flavour changing scattering (from p 0 to p /a)! 16 Action with quarks S dUd[d ] e (Sg M ) dU (det M) e Sg M : matrix of dynamical quark masses and depends on the quark formulatio n det M causes big numerical problems!! Quenched approximat ion Forget about thedynamics of sea quarks chiral extrapolat ion Work with heavier quarks and extrapolat ion of light quarks like u and d 17 Relating lattice results to physics Make the correlators of quarks by using matrices r 0 ( ) 0 T ( ) T mesons with spin ( 5 ) 0 ( 5 ) T pseudoscalar ( i ) 0 ( i ) T vector relative spatial distribution (r) : . . (x) (r) ( x r ) Pr obability Density of quarks Hadron masses 18 Steps of typical lattice calculation 1- choose the lattice spacing - close to the continuum - computation costs 2- Choose a quark formulation and number of quark flavors 3- generating an ensemble of gluon configurations - Try to go near small masses - computation costs 4- calculation of quark propagators on each gluon configuration 5- combination of quark propagators to form hadron correlators 6- Determination of lattice spacing in Gev(lattice calibration) 7- extrapolation of hadron masses as a function of bare quark masses 8- repeat the calculation using several lattice spacing to compare with physical results at the limit of a 0 9- compare with experiment or give a prediction for experiment 19 Some results of lattice QCD calculations The spectrum of light mesons and baryons in the quenched approximation 20 The ratio of inverse lattice spacing 21 The massesof and K* mesonsas a functionof lattice spacing 22 c JPC Charmonium spectrum in quenched approximation 23 Summary - Photons don’t carry any colour charge, so QED is analytically solvable. - Gluons do carry colour charge,so to solve the QCD theory, approximations are proposed (e.g. Lattice calculation method ). - There is a fermion doubling problem in lattice which can be solved by various methods. - In order to obtain light quark properties, we need bigger computers and the calculation costs will be increased. - Quenched approximation is reasonable in order to decrease the computation costs. 24