* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In plants which portion occurs transpiration?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
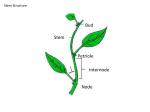
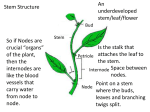
Chapter nine Plant Physiology Plants have plenty of tiny pores to occurs some physiological process. Excess of water is lost from this pores. define the transpiration; described the structure of stomata & its mechanism; analysis the important of stomata. Transpiration The physiological process by which the loss of excess water in the form of water vapour through aerial parts of the plant is called transpiration. Types of transpiration Stomatal transpiration: through the stomata. about 90-95% of transpiration occurs by this way. Cuticular transpiration: through the cuticle. About 5% occurs by this way. Lenticular transpiration: through the lenticel. About 1% occurs by this way. Stomatal transpiration process The water absorbed by root hairs rises up to the xylem vessels Translocated up to the spongy and palisade parenchyma Its form a vapour When stomata open the water vapour comes out Soil water Absorption xylem vessels air cavity of leaves outside the leaf Significance of transpiration in plant life Absorption water Upward conduction of water & sap Salt absorption Photosynthesis Regulation of leaf temperature Rainfall Cell division Physical growth Prevent from germ infection Osmosis Stomata Stomata are plenty of tiny pores found in leaves. It stands at aerial parts of plants & help to gas exchanges. Position Floating aquatic plants upper surface Submerged leaves lack stomata entirely Xerophytes plants have sunken stomata Dicotyledons plants have more stomata on the lower epidermis than upper portion Monocotydons plants have same number of stomata on both epidermis Structure subsidiary cells Guard cell outer thin wall inner thick wall a nucleus plenty of chloroplast Mechanism of opening & closing stomata Endosmosis enters H2O in guard cell open stomata Exosmosis closed stomata out of H2O in guard cell turgid guard cell flaccid guard cell Lloyd’s theory Lloyd (1908) introduced this theory. He proved that opening & closing stomata depend on the variation of osmotic pressure and interchange of starch & sugar is the cause of that. Insoluble starch in guard cell Exosmosis of water Soluble sugar Endosmosis of water Decrease osmotic pressure Flaccid guard cell Increase osmotic pressure Turgid guard cell Closed stomata Open stomata Sayre’s theory Sayre (1926) introduced this theory. He proved that opening & closing stomata depend on the inter change between sugar & starch and PH is the cause of that. In day time Starch converted glucose-1phosphate Increase osmotic pressure At night Turgid guard cell glucose-1phosphate converted Starch Decrease osmotic pressure Flaccid guard cell PH goes up to 7.5 Open stomata PH falls to 5 Closed stomata Modern theory Lexitt (1974) introduced this theory. He proved that K+ is the cause of opening & closing stomata. Night , K+ & H2O out of, osmotic pressure decrease Open stomata Closed stomata Light , K+ & H2O enters, osmotic pressure increase Individual Work: According to Sayre’s theory what is causes for opening & closing stomata? Write down the importance of tomata in plants. In plants which portion occurs transpiration? By which process the transpiration take place? On basis of transpiration way how many types of transpiration ? Which type of chemical substances made a cuticle? In where the plants give out about 90-95% water in form of vapour? In which process about 5-10% water given out in the form of vapour? Which part of plant is the main organ of transpiration? How many guard cell adjacent the stomata? Which layer of guard cell is thick? How many nucleus contains each guard cell?