* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Delivery Course - University of Pittsburgh
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
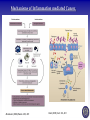
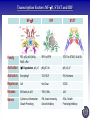
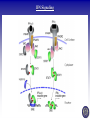
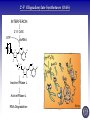
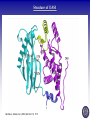
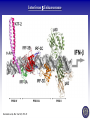
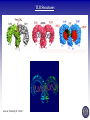
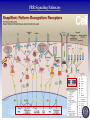
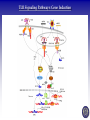
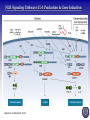
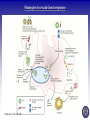
Tumor Virology Course: MSMVM 3435, Dec 2, 2009. Who Am I? Saumendra N. Sarkar, Ph.D. (Saumen) University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, HCC 1.8 5117 Centre Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Phone: (412) 623-7720, Fax: (412) 623-7715 E-mail: [email protected] Web: http://labs.mmg.pitt.edu/sarkar/ What Am I going to talk about? And Why? • Innate Immunity, Inflammation and tumorigenesis. • Host responses to virus infection • Innate immune response to virus o Interferons (IFN) o Viral components and their Sensors o TLR, RLR, NLRs • Innate Immune evasion strategies of viruses Evolution of the “central dogma” for Cancer. Weinbarg, 2000 Examples: • Helicobacter pylori (Marshall & Warren, 2005) • Human papillomavirus (zur Hausen, 2008) • Hepatitis B and C virus Karin, Mantovani, 2006.. Mechanisms of Inflammation mediated Cancer. Montavani (2008) Nature. 454, 436 Karin (2006) Cell. 124, 823 Kinetics of immune response after virus infection Biron & Sen (2007) Fields Virology Interferons Type I (a1, a2.., b, d, e, t, k..) Size Type II (g) ~ 18 kDa 21 kDa Cell Source Most Nucleated cells Activated T Cells, NK Cells Target Cells All Monocytic Cells and others Mainly Antiviral Antiviral and Antitumor IFNAR IFNGR Effect Receptor Transcription Factors: NF-kB, STAT and IRF NF-kB IRF STAT Family P50, p52, p65 (RelA), RelB, c-Rel IRF1 to IRF9 STAT1 to STAT6; 5A & 5B Activation IkB Degradation, pS, pT pS, pT, Ub pY, pS, pT Activators Everything!! TLR, RLR IFN, Hormone Repressor IkB Not Clear SOCS Kinases IKK family to IkB TBK1, IKKe JAK Genes Cytokines, Inflammation, Growth Promoting IFN, Innate Immunity, Growth Inhibitory ISGs, Growth Promoting/Inhibitory. IFN Signaling Protein Kinase RNA activated (PKR) Enzyme: Ser/Thr kinase, Activator dsRNA, PACT (cofactor) Substrate: eIF2a, PKR, other substrates in vitro. Function: Translation inhibition, other PKR Structure PKR Activation 2’-5’ Oligoadenylate Synthetases (OAS) INTERFERON 2’-5’ OAS ATP dsRNA O O O P O 3 N O 5 3 N N 2 N N O O O P O O N O 5 3 N N 2 N O O Inactive RNase L Active RNase L RNA Degradation N Structure of OAS1 Hartmann, Sarkar et al. (2003) Mol Cell. 19, 1173 Other ISGs ISG56 Family: Human ISG 56, 54, 60, aka IFIT Interaction with eIF3, translation inhibition ADAR: RNA-Specific Adenosine Deaminase A || U Mx/GBP: small GTP binding proteins ISG15: Similar to Ubiquitin I || U I || C Virus - dsRNA – Interferon – anti-viral state Interferon b Enhansosome PRD IV Escalante et al, Mol. Cell 26, 703-16 PRD III-I PRD II Toll-like Receptors TLR Structures Jin et al, Immunity 29, 182-91 NLRs, RLRs Inflammosomes PYD: Pyrin NACHT: used to be called NOD NOD: Nucleotide Oligomerization NAD: NACHT Associated CARD: Caspase Recruitment LRR: Leucine Rich Repeat BIR: Baculovirus IAP Repeat. Meylan et al, Nature 442, 39-44 Cellular Sensors of DNA and DNA viruses • DNA transfection induces IFNb independent of TLRs (Stetson, 2005) • Cytoplasmic DNA sensor – DAI/ZBP1 (Takaoka, 2007) o o Transient Expression allows DNA dependent IRF activation, siRNA. DAI interaction with DNA • NALP3/ASC Inflammosome (Muruve, 2008) o o Adenoviral particles, capsid, DNA induced IL-1 secretion in a NALP3, ASC dependent manner. No IRF activation. • AIM2, new protein which interacts with ASC (Hornung, 2009) o Binding, localization with ASC o Direct DNA binding o IRF activation? • RNA polymerase III, transcribes dA.dT to RNA for RIG-I recognition (Hornung, 2009/Chen, 2009) o 5’pppN is important PRR Signaling Pathways TLR Signaling Pathways: Gene Induction RLR Signaling Pathways: Gene Induction Takeuchi and Akira Curr. Opin. Immun. 20, 17-22 NLR Signaling Pathways: IL-1 Production & Gene Induction Meylan et al, Nature 442, 39-44 Viral Evasion Strategies to evade host response Finlay et al, Cell 124, 767 Examples of Viral Evasion TLR/RLR IFN ISG Pox V IFNARs IFNGRs TNFR Flu NS1 Paramyxo V, W HCV NS3/4A Adeno VAI RNA Mu V Nipah W Adeno E1A EBNA1 HHV8 K9 HPV E6 Adeno VAI RNA EBV EBER RNA HIV TAR RNA Vaccinia E3L Multifunctional viral proteins with multiple targets!! Paramyxo V and W, Flu NS1, Adeno E1A, SV40 T…… Putting it together Natural Selection References • Innate Immunity, TLR, NLR o o o Immunity's Early-Warning System, Luke A. J. O'Neill, Scientific American, Jan 2005. (@ sarkarlab/research) Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response, Ruslan Medzhitov, Nature, Oct 18, 2007 (PMID: 17943118) Akira, S., Uematsu, S., and Takeuchi, O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124, 783-801. (PMID: 16497588) • Infalammation Cancer o o Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Michael Karin, Toby Lawrence, and Victor Nizet Cell 124 (4), 823-35 (PMID: 16497591) Cancer-related inflammation. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Nature. 454: 436 (PMID: 18650914) • Viral Evasion o o Pathogen subversion of cell-intrinsic innate immunity. Roy CR, Mocarski ES. Nat Immunol. 8:1179 (PMID: 17952043) Viral evasion and subversion of pattern-recognition receptor signalling. Bowie AG, Unterholzner L. Nat Rev Immunol. 8: 911(PMID: 18989317) My Assessment • • • • I think it was pretty good. How to keep people falling off to sleep? Make people more interactive during the class Incorporate more stories and experiments describing how some of these were discovered.