* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ABO BLOOD GROUPS
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
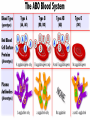
ABO BLOOD GROUPS CHAPTER 4 P. 83-86 ABO Blood groups are a case of Multiple Alleles ABO blood groups are a case of multiple alleles where there are three alternative alleles for one gene Discovered by Karl Landersteiner in the early 1900’s Controlled by a gene located on c-some 9. One combination of alleles in the ABO system exhibits codominance. How is the ABO blood complex determined? ABO phenotype is ascertained by mixing a blood sample with antiserum containing type A or B antibodies Antigen – molecule ( often a surface protein), that is capable of elliciting the formation of antibodies Antibody – Protein (Immunoglobulin) produced in response to an antigenic stimulus binds to antigen If the antigen is present on the surface of the person’s red blood cells, it will react with the antibody causing clumping or agglutination of the red blood cells Phenotypes The 4 possible Phenotypes are A antigen ( A Phenotype) B antigen ( B Phenotype) AB (A and B antigens presentAB Phenotype) O (no antigensO Phenotype) Isoagglutinogen The ‘I’ designation is utilized for isoagglutinogen, another term for antigen IA – A blood B antibody I B – B Blood A Antibody IAB - AB Blood No Antibodies Universal Recipient (i)IO – O Blood A and B Antibodies present Universal Donor IA and IB behave dominantly to IO but behave codominantly to each other Rh Antigens Rh antigens were also thought to illustrate multiple allelism Important because of their involvement in the disorder Erythroblastosis fetalis Form of Anemia Occurs when mother is Rh- and father is Rh+ and those factors contribute to the allele of the fetus This combination results in an immunological incompatibility of the mother and the fetus If the fetal blood passes through a ruptured placenta at birth and enters the maternal circulation, the mother’s immune system will recognize the Rh antigen from the fetal blood and build immunities against it. During a second pregnancy, the antibody concentration becomes high enough that when they pass across the placenta into fetal circulation they will begin to destroy the fetal blood cells – fatal to fetus Preventative Measures Rh – mothers are given anti-sera Destroys Rh-positive cells that may have entered the mother’s circulatory system Rh Factors and blood typing reference